Browse by specialty
- Anesthesia and Perioperative
- Cardiology & Cardiovascular System
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Dermatology
- Diagnostic Imaging
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethical, Legal, and Organizational Medicine
- Family Medicine
- Gastroenterology
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- Gynecology
- Haematology
- Infectious Disease
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pediatrics
- Plastic Surgery
- Population and Community Health
- Psychiatry
- Respirology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
Diagnostic Imaging
Practice Cases
Appendicitis: A Radiology Case Report
Jeffrey Lam Shin Cheung, Tania Saha, Dr. Nasir Jaffer
Presentation
Sujata is a 24-year-old female presenting to the emergency room with a six-hour history of right-side lower quadrant abdominal pain. She notes that she is experiencing pain that originated from her umbilicus that now radiates diffusely with increasing intensity across the lower abdomen. Sujata describes her pain as sharp and colicky. She discloses feeling nauseous and vomiting prior to entering the emergency room. Her pain is slightly relieved by an over-the-counter analgesic and by leaning forward. However, she notes that it is exacerbated by extension of the right hip.
Physical Examination
On physical examination of Sujata, right lower quadrant pain is noted on palpation at the junction of the lateral third and medial two-thirds of a line drawn from the anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus. A positive psoas sign is noted as she experiences pain on passive extension of her right hip when she lies on her left side. She has no other significant findings on physical examination.
Imaging
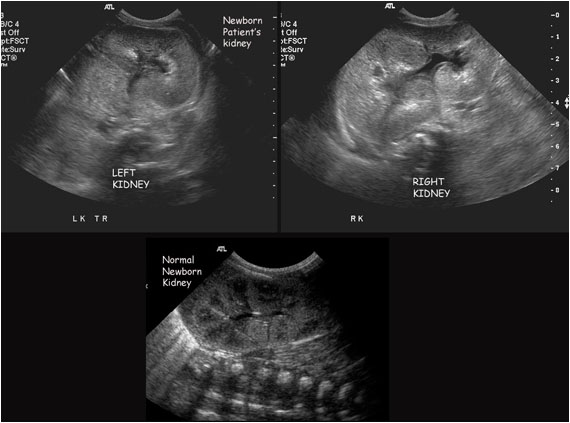
An ultrasound of the abdomen is done as the first-line imaging and if there are non-benign appreciations, a CT is completed.
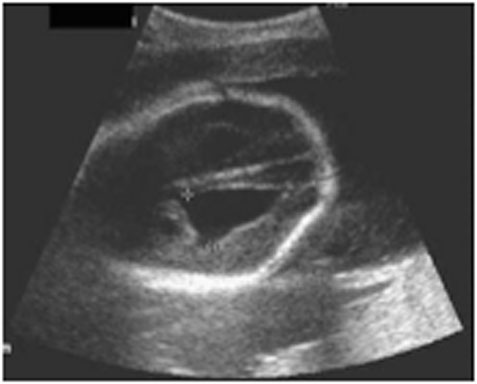
An ultrasound shows thick-walled appendix, appendicolith, dilated fluid-filled appendix, and be non-compressible.
A CT will show enlargement of the appendix (>6 mm in outer diameter), enhancement of the appendiceal wall, and appendicolith.

Figure 1. Ultrasound of acute appendicitis.
Variations in Presentation and Differential Diagnoses
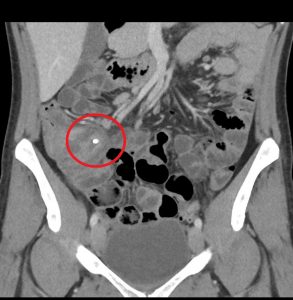
Figure 2. Appendicitis may present with appendicolith, a type of fecalith in the appendix. In a CT scan, this will appear as a calcified mass, typically in the appendiceal lumen.
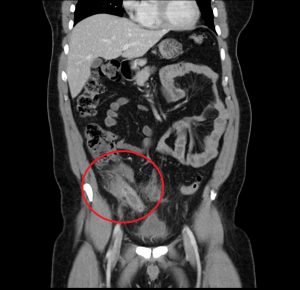
Figure 3. A mucocele of the appendix appears as a dilated, mucin-filled appendix, and may mimic the appearance of appendicitis.
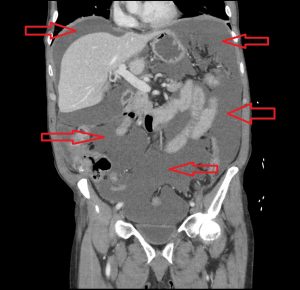
Figure 4. A mucocele of the appendix may also result in pseudomyxoma pertionei, a mucinous tumour that spreads throughout the peritoneal cavity. The incidence is 1-3/1,000,000 annually.
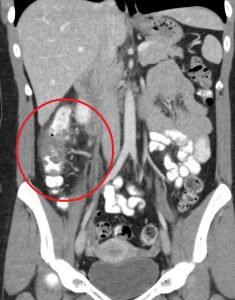
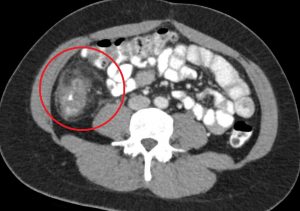
Figure 5. Cecal diverticulitis has a similar clinical presentation as appendicitis. On CT imaging, both may demonstrate a dilated appendix with periappendiceal fat stranding. In cecal diverticulitis, however, one would expect to see diverticula (outpouchings) in the cecum/ascending colon with associated fat stranding.
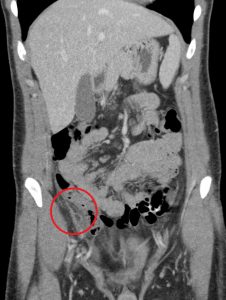
Figure 6. Epiploic appendagitis has a similar clinical presentation as appendicitis. A typical finding on CT includes a hyperattenuating ring around the inflamed epiploic appendage.
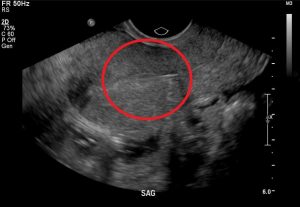
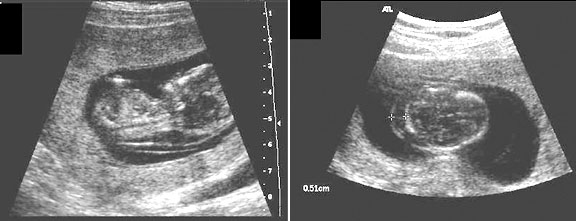
Figure 7. It is imperative to rule out ectopic pregnancy in a female patient presenting with abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. A high β-HCG (>6500 IU/l) and ultrasound showing an empty uterus (with possible decidual reaction) is suggestive of an ectopic pregnancy.
Practice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following imaging findings is most suggestive of a ruptured appendix on CT scan imaging?
- Periappendiceal abscess
- Small bowel diameter of 5cm
- Thickened cecal wall
- Thumbprinting in the ascending colon
Answer: 1
Explanation: Periappendiceal abscess and extraluminal gas are two common signs of a perforated appendix. A small bowel diameter >3cm is considered dilated and may be due to an obstruction or adynamic ileus. A thickened bowel wall is a nonspecific sign that may be caused by inflammation, infection, and ischemia among other causes. Thumbprinting in the colonic wall is suggestive of colitis.
Question 2. Which of the following features is not commonly associated with appendicitis on CT scan imaging?
- Dilated (>6 mm), fluid-filled appendix
- Multiple sacculations within the cecal wall
- Thickening of the cecal apex
- Perpendicular fat stranding surrounding the cecum
Answer: 2
Explanation: Multiple sacculations within the colonic wall in a patient presenting with acute abdominal pain is more suggestive of diverticulitis. A dilated, fluid-filled appendix is the most specific CT finding of appendicitis. Thickening of the cecal appendix may be a secondary sign of appendicitis, and fat stranding is a nonspecific finding that may be seen in appendicitis among other conditions such as inflammation, infection, and ischemia of the bowels.
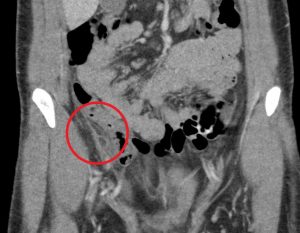
Question 3. A 33-year-old man has right lower quadrant abdominal pain radiating to the right upper quadrant. A CT scan is ordered and reveals the following.
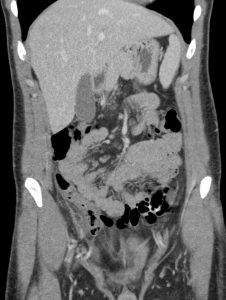
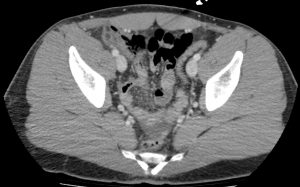
What treatment choice would you recommend?
- Conservative management
- Laparoscopic appendectomy
- Piperacillin and tazobactam
- NPO order for 24 hours
Answer: 1
Explanation: The fat density mass near the ileocecal junction, which also demonstrates the hyperattenuating ring sign, is suggestive of epiploic appendagitis. Conservative management with analgesics is often sufficient. Laparoscopic appendectomy may be considered for appendicitis, and antibiotic treatment may be appropriate for appendicitis or complicated diverticulitis. An NPO order may be considered for uncomplicated diverticulitis.
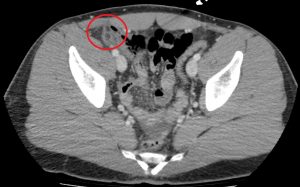
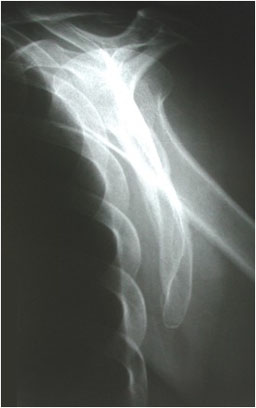
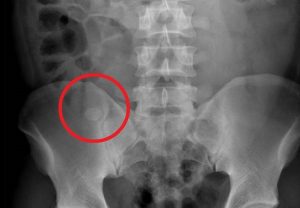
Question 4. A patient in a rural town presents to their doctor with a 3-day history of RLQ pain and nausea. Their doctor orders an x-ray that reveals the following.
This patient has an increased risk of all of the following except:
- Acute appendicitis
- Constipation
- Abscess formation
- Appendix perforation
Answer: 2
Explanation: This x-ray demonstrates a large calcified mass in the right lower quadrant, which is suspicious for an appendicolith (a type of fecalith occurring in the appendix). An appendicolith itself does not typically cause bowel obstruction or constipation, though a low-fiber diet increases the risk of fecalith formation.
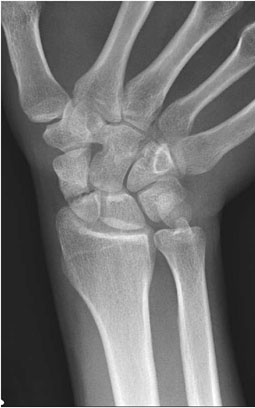
Question 5. A 44-year-old female complains of abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. An ultrasound is ordered and reveals the following.
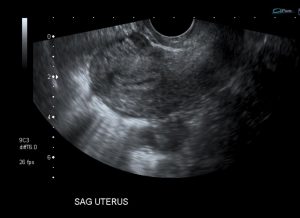
Which of the following is the next best course of action?
- Order an urgent CT
- Tell the patient that no further management is needed
- Refer the patient for a hysterectomy
- Order lab investigations
Answer: 4
Explanation: The patient’s older age and symptoms are concerning for an ectopic pregnancy. The ultrasound shows an empty uterus with decidual reaction (thickening of the endometrium), which further supports a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. A β-hCG should have been ordered for this patient, and the typical expected value would be >6500 IU/l in a case of ectopic pregnancy.
References
Hardin Jr DM. Acute appendicitis: review and update. American family physician. 1999 Nov 1;60(7):2027.
Rizvi SA, Syed W, Shergill R. Approach to pseudomyxoma peritonei. World journal of gastrointestinal surgery. 2018 Aug 27;10(5):49.
Gaitini D. Imaging acute appendicitis: state of the art. Journal of clinical imaging science. 2011;1.
Pereira JM, Sirlin CB, Pinto PS, Jeffrey RB, Stella DL, Casola G. Disproportionate fat stranding: a helpful CT sign in patients with acute abdominal pain. Radiographics. 2004 May;24(3):703-15.
Subramaniam R. Acute appendagitis: emergency presentation and computed tomographic appearances. Emergency Medicine Journal. 2006 Oct 1;23(10):e53-.
Kaya B, Eris C. Different clinical presentation of appendicolithiasis. The report of three cases and review of the literature. Clin Med Insights Pathol. 2011;4:1-4. Published 2011 Mar 30. doi:10.4137/CPath.S6757
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Ruptured Posterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm
Tiffany Ni, Raza Syed, Dr. Kieran Murphy
Introduction
Cerebral aneurysms result from an abnormal focal dilation of an artery wall in the brain and can vary in size from 0.5 mm to greater than 25 mm(1,2). While most cerebral aneurysms are silent and may be incidentally identified on imaging, aneurysmal rupture is commonly associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), leading to a high morbidity and mortality rate(1,2).
Despite the current uncertainties surrounding the precise mechanisms by which cerebral aneurysms develop, grow, and rupture, several factors have been associated with the formation of cerebral aneurysms(3,4). Some include hypertension, age over 40, smoking, trauma to the blood vessels, and a family history of aneurysms(3).
Posterior communicating artery (PCOM) aneurysms are the second most common aneurysms overall, accounting for 25% of all aneurysms and representing 50% of all internal carotid artery (ICA) aneurysms(5). We report a patient with a ruptured left PCOM aneurysm presenting with a left subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Patient presentation
A 52-year-old woman was presented with a sudden onset of severe headache, vomiting, nuchal rigidity, and decreased conscious level. She was transported to our hospital for management of subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH). On admission, the patient was semi-comatose with anisocoric pupils, and a Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score of 5. She had no past medical history of trauma, hypertension, diabetes or other diseases.
Investigations & Diagnoses
Based on the patient’s clinical presentation, the following would be included in the list of differential diagnoses(1):
- Arteriovenous malformations
- Cavernous sinus syndromes
- Carotid/vertebral artery dissection
- Cerebral venous thrombosis
- Fibromuscular dysplasia
- Migraine and cluster headaches
- Moyamoya disease
- Pituitary apoplexy
- Stroke - ischemic or hemorrhagic
- Vein of Galen malformation
The first-line diagnostic investigations to be ordered included(6):
- conventional catheter-based angiogram (digital subtraction angiography)
- CT angiography
- magnetic resonance angiography
The repeat computerized tomography (CT) scan demonstrated diffuse subarachnoid hemorrhage (Figure 1). Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) confirmed the presence of a saccular aneurysm localizable to the PCOM on the left side (Figure 2).
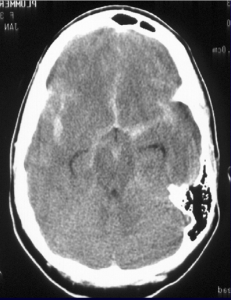
Figure 1. Computed tomographic scan showing diffuse subarachnoid bleeding secondary to rupturing of the PCOM aneurysm
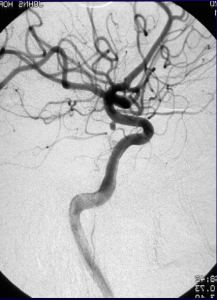
Figure 2. Digital subtraction angiography was performed which showcases an aneurysm originating from the PCOM
Procedure
Endovascular detachable coil embolization was performed under intravenous anesthesia. The microcatheter was navigated from the femoral artery to the left PCOM aneurysm and a microcatheter tip was positioned in the aneurysm under fluoroscopic guidance. Coil position within the aneurysm and the patency of the parent vessel were confirmed angiographically prior to every coil detachment. The left PCOM aneurysm was successfully occluded (Figure 3).
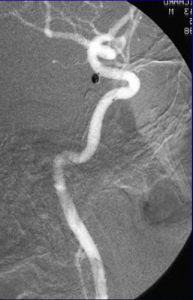
Figure 3. Digital subtraction angiography was performed following endovascular coiling of the PCOM aneurysm showing complete occlusion of the aneurysm and exclusion from circulation as well as good patency of the PCOM
One week later, follow-up CT and DSA examination was performed and revealed no abnormality in the brain parenchyma and good patency of the PCOM. The patient’s postoperative course was uneventful, and she was discharged home on the 14th postoperative day. The patient was neurologically intact at discharge.
Case Questions
What if the patient in this case was 35 years old instead? How would your treatment strategy change?
- endovascular coiling
- anti-platelet medications only
- surgical clipping
- endovascular thrombectomy
Answer: 3) surgical clipping (instead of endovascular coiling)
In endovascular coiling, a micro-catheter is inserted into the femoral artery via an initial catheter(7,8). A platinum coil is attached to the microcatheter tip. When the microcatheter reaches the lumen of the aneurysm, an electrical current is used to separate the coil from the catheter. The coil induces thrombosis of the aneurysm and is left permanently in the aneurysm.
Surgical clipping is done under general anesthesia and requires open surgery(7). The brain is gently retracted to visualize the aneurysm. A small clip is placed across the neck of the aneurysm to block the blood flow into it. Clips are made of titanium and remain on the artery permanently.
In this situation, the preferred method of treatment would be surgical clipping(9). The less invasive nature of coiling is likely to be favored in patients who are older, are in poor health, have serious medical conditions, or have aneurysms in certain locations. In patients younger than 40 years of age, the difference in the safety between coiling versus clipping is small. Therefore, the better long-term protection from bleeding may give patients with clipped aneurysms an advantage in life expectancy.
What imaging technique should be used to assess any possible residual perfusion of the aneurysm?
- non-contrast enhanced CT scan
- magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
- CT angiography
- digital subtraction catheter angiography
Answer: 4) Digital subtraction catheter angiography
Digital subtraction catheter angiography remains the gold standard for diagnosis and characterization of vascular abnormalities and in many centers, even if the causative lesion is identified on MRA or CTA and it is thought to require surgical management, a catheter study is carried out(10).
The benefit of DSA over MRA or CTA is two-fold:
- Higher spatial resolution: better able to delineate small vessels and characterize vascular morphology (e.g. aneurysm neck and incorporation of adjacent vessels)
- Temporal resolution: contrast can be seen to wash into and out of vascular malformations, giving important information in regard to the feeding vessels (e.g. arteriovenous malformations or dural arteriovenous fistulas)
A non-contrast enhanced CT scan is commonly used as the first-line imaging modality for evaluating subarachnoid hemorrhage as it is rapid, inexpensive, and widely available.
What are the characteristics of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)?
- Headaches, nausea, and vomiting is always present
- Loss of consciousness is always present
- Patients tend to present as asymptomatic
- Varies, specific syndromes have been associated with particular aneurysmal locations
Answer: 4) Varies, specific syndromes have been associated with particular aneurysmal locations.
For example, aneurysms at the anterior communicating artery, the most common site of aneurysmal SAH (34%), have the following characteristics(11):
- These aneurysms are usually silent until they rupture
- Suprachiasmatic pressure may cause altitudinal visual field deficits, abulia or akinetic mutism, amnestic syndromes, or hypothalamic dysfunction
- Neurologic deficits in aneurysmal rupture may reflect intraventricular hemorrhage (79%), intraparenchymal hemorrhage (63%), acute hydrocephalus (25%), or frontal lobe strokes (20%)
What is the progression of aneurysmal rupture?
- Aneurysmal rupture is typically self-limiting
- Aneurysmal rupture results in vasodilation
- Aneurysmal rupture typically results in SAH
- Aneurysmal rupture results in hypernatremia
Answer: 3) Aneurysmal rupture typically results in SAH.
What typically accompanies the SAH is diffuse or focal forms of vasospasm that may lead to ischemia and infarction11.
Recent animal data suggest therapeutic benefit of nitrite infusions to enhance cerebral perfusion in the setting of aneurysmal SAH11. This delayed complication of vasospasm is of unclear pathogenesis but most likely is due to the presence of blood and the formation of multiple substances in the subarachnoid space. Spontaneous thrombosis of an aneurysm and subsequent recurrence have been reported in a few cases.
What are possible complications of ruptured cerebral aneurysms in general?
- Seizures
- Hyponatremia
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
- All of the above
Answer: 4) All of the above.
Some of the other complications of ruptured cerebral aneurysms include11:
- Vasospasm
- Recurrent hemorrhage
- Hydrocephalus
- Cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, or congestive heart failure
- Neurogenic pulmonary edema, pneumonia, or atelectasis
- Anemia
- Venous thromboembolism
References
- Jersey AM, Foster DM. Cerebral Aneurysm. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 [cited 2021 Jun 24]. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507902/
- Cianfoni A, Pravatà E, Blasi RD, Tschuor CS, Bonaldi G. Clinical presentation of cerebral aneurysms. Eur J Radiol. 2013 Oct 1;82(10):1618–22.
- Inagawa T. Risk factors for the formation and rupture of intracranial saccular aneurysms in Shimane, Japan. World Neurosurg. 2010 Mar 1;73(3):155–64.
- Etminan N, Buchholz BA, Dreier R, Bruckner P, Torner JC, Steiger H-J, et al. Cerebral aneurysms: Formation, progression and developmental chronology. Transl Stroke Res. 2014 Apr;5(2):167–73.
- July J. Surgery of Posterior Communicating Artery Aneurysm. In: July J, Wahjoepramono EJ, editors. Neurovascular Surgery : Surgical Approaches for Neurovascular Diseases [Internet]. Singapore: Springer; 2019 [cited 2021 Jun 24]. p. 87–92. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8950-3_11
- Cerebral aneurysm - Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment | BMJ Best Practice US [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jun 24]. Available from: https://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-us/490
- Kim K-H, Cha K-C, Kim J-S, Hong S-C. Endovascular coiling of middle cerebral artery aneurysms as an alternative to surgical clipping. J Clin Neurosci. 2013 Apr 1;20(4):520–2.
- Kim YJ, Song KY. Endovascular Coiling of Multiple (More than Four) Intracranial Aneurysms. Interv Neuroradiol. 2004 Mar;10(1):75–81.
- Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, Sandercock P, Clarke M, Shrimpton J, et al. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet Lond Engl. 2002 Oct 26;360(9342):1267–74.
- Chen SH, Sur S, Sedighim S, Kassi A, Yavagal D, Peterson EC, et al. Utility of diagnostic cerebral angiography in the management of suspected central nervous system vasculitis. J Clin Neurosci Off J Neurosurg Soc Australas. 2019 Jun;64:98–100.
- Chen J, Li M, Zhu X, Chen Y, Zhang C, Shi W, et al. Anterior Communicating Artery Aneurysms: Anatomical Considerations and Microsurgical Strategies. Front Neurol. 2020;11:1020.
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Congestive Heart Failure
Ashraf Altesha, Sandra Sabongui, Muhammad Uzair Khalid, Dr. Ciara O’Brien
A 67-year-old female presented to the emergency department with worsening shortness of breath (SOB) and a persistent cough. She first noticed the SOB while climbing one flight of stairs approximately one month ago. Her symptoms have become progressively worse since, with SOB upon taking 15-20 steps on a flat surface and performing household tasks such as sweeping the floor. She takes breaks often to catch her breath, and has to sleep in a recliner due to SOB while lying flat. She also reports recent weight gain, fatigue, swelling in her feet and ankles, and a progressive dry cough for one month. She denies sick contacts, fever, chills, wheezing, hemoptysis, chest pain, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. The patient’s past medical history is significant for hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and obesity (BMI 32). Medications include Metformin 1000 mg BID, Sitagliptin 100 mg OD, and Amlodipine 10 mg OD. She does not smoke, consume alcohol or use any recreational drugs. Her family history is unremarkable.
On physical examination, she was alert with a Glasgow Coma Scale of 15. She was tachypneic in tripod position with a respiratory rate of 24 and SpO2 of 91% on room air. HR was 110 bpm and regular, BP 154/92, and she was afebrile at 36.6°C. Her cardiac examination revealed distant heart sounds with a 3/6 holosystolic murmur best appreciated in the mitral region. Bilateral inspiratory crackles were present on auscultation, with reduced air sounds at the lung bases and dullness to percussion. Lower extremities had 2+ pitting bilaterally to the mid shins with palpable pulses. JVP was 6 cm above the sternal angle with a positive hepatojugular reflux.
Initial investigations included CBC, electrolytes, LFTs, creatinine, BNP, Troponins, ECG, and CXR. Pertinent findings included hyponatremia with Na of 132, an AKI with creatinine of 110 (baseline low 80s), and BNP of 520. ECG showed sinus tachycardia (114 BPM), and CXR findings included bilateral pleural effusions, cardiomegaly and features of interstitial and alveolar pulmonary edema including air space opacification, vascular redistribution, peribronchial cuffing, and Kerley B lines. An echocardiogram was obtained and showed moderate mitral regurgitation with EF of 44%. A diagnosis of CHF exacerbation was made. Patient was placed on 2L oxygen via nasal prongs, given 40 mg of IV furosemide and 60 mg of nitroglycerin over 24h via transdermal patch. Furosemide was continued BID for 2 more days until resolution of hyponatremia, AKI, and clinical improvement with euvolemia. Patient was then discharged on a standing dose of Furosemide 20mg BID, in addition to medications for chronic management of CHF including Ramipril 1.25mg OD, and Metoprolol 25mg OD and advised to follow up with primary care provider for titration of medications to achieve target blood pressure control.
Figures:
Figure 1: Kerley B lines (Shown by the red arrows) are thickened interlobular septa that are 1-2 cm long and 1 mm thick caused by interstitial fluid infiltration. They can be found at the lung bases or periphery, perpendicular to the pleural surface. Kerley B lines can be seen in pulmonary edema, pneumonia, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, and lymphangitis carcinomatosa.
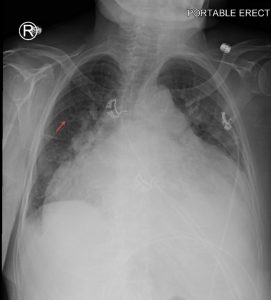
Figure 2: Peribronchial cuffing or “doughnut sign” (shown by the red arrow) is used to describe the increased density around a bronchus or large bronchiole caused by increased fluid or mucus buildup. This sign can be observed in plain films or head-on in CT scan. The differential for peribronchial cuffing is broad, and can include acute bronchitis, asthma, bronchiolitis, congestive heart failure, cystic fibrosis, diffuse parenchymal lung disease, Kawasaki disease, lung cancer, pneumonia, pulmonary edema, and smoke inhalation.
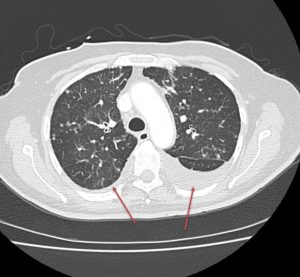
Figure 3: Pleural effusion (red arrows) is the accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural space surrounding the lung. This occurs when the influx rate of fluid into the pleural space exceeds the efflux rate, and may be caused by changes in Starling forces favouring fluid extravasation (eg. congestive heart failure and liver failure), obstruction of lymphatics (eg. malignancy), or leakage of fluid from elsewhere (eg. hemothorax, chylothorax, or urinothorax). The differential for a transudative effusion includes congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, and liver failure. An exudative effusion results from disruption to the pleura and the commonest causes are cancers, and infection.
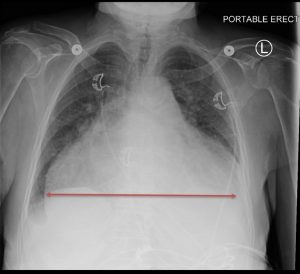
Figure 4: Cardiomegaly is defined as a transverse diameter of the cardiac silhouette that is greater than or equal to 50% of the chest transverse diameter (cardiothoracic ratio ≥ 0.5) on a posteroanterior chest X-ray or CT scan. This is caused by dilatation and hypertrophy of the heart muscle, which may be due to long-standing hypertension, coronary artery disease, valvular disease, infection, or cardiomyopathy. The differential diagnosis for cardiomegaly includes pericardial effusion, an anterior mediastinal mass, a prominent epicardial fat pad, and mediastinal widening secondary to a pulmonary or aortic pathology.
Multiple Choice:
- Which one of the following signs on CXR refers to the finding of a well-rounded left ventricle and dilated aorta indicative of left ventricular hypertrophy?
- Fleischner sign
- Hampton hump
- Shmoo sign
- Water Bottle sign
Answer: 3
- On a chest x-ray, findings indicative of right ventricular hypertrophy include:
- Rounded left heart border
- Uplifted cardiac apex
- Rotation of the heart posteriorly
- All of the above
Answer: 4
- Which one of the following signs refers to bilateral perihilar airspace opacities on CXR which can be found in pulmonary edema?
- Stag’s antler sign
- Hampton hump
- Bat wing sign
- Comet tail sign
Answer: 3
- On x-ray, a mediastinal mass consistent with malignancy was found with unilateral pleural effusion. The effusion was tapped under ultrasound guidance by an interventional radiologist. What do you expect to find?
- Transudate; Pleural to serum protein ratio should be greater than 0.2.
- Transudate; Pleural to serum protein ratio should be greater than 0.5.
- Exudate; Pleural to serum protein ratio should be greater than 0.2.
- Exudate; Pleural to serum protein ratio should be greater than 0.5
Answer: 4
- What if the patient was an ex-smoker and a diagnosis of COPD exacerbation was made, what are some signs you may see on physical exam and CXR?
- Barrel chest, hyperinflation, diaphragmatic flattening, and air bronchograms
- Pectus carinatum, Kerley B lines, vertical and narrow heart, and hyperinflation.
- Barrel chest, vertical and narrow heart, diaphragmatic flattening, and hyperinflation.
- Barrel chest, bullae, meniscus sign, and hyperinflation.
Answer: 1
References
- Gluecker T, Capasso P, Schnyder P, Gudinchet F, Schaller M, Revelly J et al. Clinical and Radiologic Features of Pulmonary Edema. RadioGraphics. 1999;19(6):1507-1531.
- Bramson R, Griscom N, Cleveland R. Interpretation of Chest Radiographs in Infants with Cough and Fever. Radiology. 2005;236(1):22-29.
- Reed J. Chest radiology. Philadelphia: Mosby; 2003.
- Karkhanis V, Joshi J. Pleural effusion: diagnosis, treatment, and management. Open Access Emergency Medicine. 2012;:31.
- Dähnert W. Radiology review manual. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams Wilkins; 2011.
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Extraluminal Gas
Hayley Good, Grace Grafham, Aiman Shahid , Dr. Ciara O’Brien
Introduction
Extraluminal gas is free air outside of the sealed gastrointestinal tract. The presence of extraluminal gas can have a broad spectrum of differential diagnoses such as peritoneal cavity infection, bowel ischemia, malignancy, trauma, and iatrogenic from abdominal surgery or recent instrumentation. The thorough evaluation of radiological findings as well as the location of the free air can help lead to a prompt diagnosis.
Clinical Case
Patient Presentation
Andrew is a 65-year-old male presenting to the emergency department with severe and diffuse upper abdominal pain, radiating to his right shoulder. The pain started suddenly and is worse with movement. He has associated nausea, vomiting, abdominal bloating, and anorexia. His past surgical history includes an appendectomy and herniorrhaphy. His past medical history includes long standing hypertension, type II diabetes mellitus, and a transient ischemic attack at the age of 55 years. His medications include ramipril, metformin, and low-dose aspirin. He has a 45-pack year smoking history.
Physical Examination
On general inspection, Andrew is in apparent distress and diaphoretic. His vital signs are as follows: blood pressure of 137/88 mmHg, heart rate of 120 bpm, respiratory rate of 18 breaths/minute, oral temperature of 37C, oxygen saturation of 98% on room air. He is peritonitic on examination with significant abdominal pain on palpation, distention, and rigidity extending to all four quadrants but most pronounced in the upper quadrants. Neck, chest, and rectal examination are all unremarkable.
Imaging
An abdominal x-ray is ordered showing subdiaphragmatic free air and right upper quadrant lucency (Figure 1). Andrew is further evaluated by CT scan prior to surgical intervention, which confirms large volume pneumoperitoneum and a defect in the anterior gastric wall (Figures 2-4). The most common cause of intraperitoneal free air (pneumoperitoneum) is hollow organ perforation due to peptic ulcer disease, diverticulitis, appendicitis, malignancy, inflammatory bowel disease, or mechanical perforation.
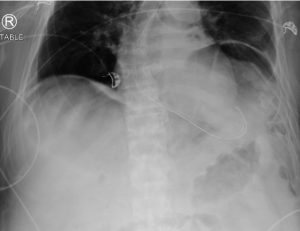
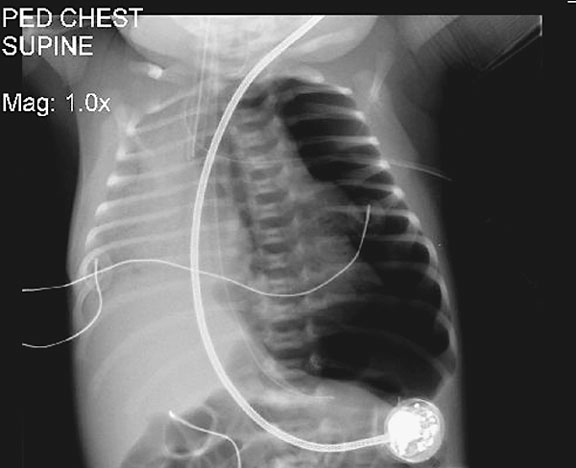
Figure 1. Abdominal x-ray showing subdiaphragmatic free air. There is lucency over the right upper quadrant anterior to the liver in keeping with pneumoperitoneum.
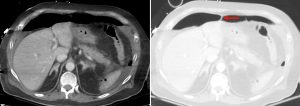
Figure 2. Axial CT of the upper abdomen with both soft tissue (left) and lung (right) windows. A large volume pneumoperitoneum can be appreciated in the lung window. As well, the falciform ligament (red arrow) which is anterior to the left hepatic lobe can be clearly visualized in the lung window.
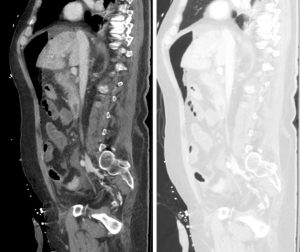
Figure 3. Sagittal abdominal CT with both soft tissue (left) and lung (right) windows. The large volume pneumoperitoneum is more easily appreciated on lung windows.
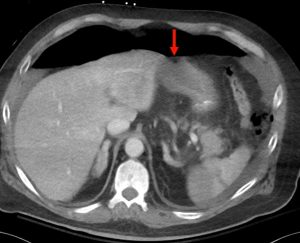
Figure 4. Axial abdominal CT demonstrating a large volume pneumoperitoneum with a defect in the anterior gastric wall consistent with perforation (red arrow).
Case Resolution
Andrew was initially managed with intravenous fluids, cessation of oral intake, opioid pain medication, and broad-spectrum antibiotics while awaiting imaging results. He was later diagnosed with a perforated gastric ulcer and received an urgent partial gastrectomy.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Radiological Signs of Intraperitoneal Free Air
Falciform ligament sign
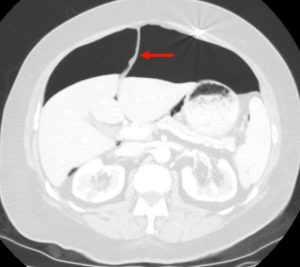
Figure 5. Axial CT of the abdomen showing falciform ligament sign (red arrow) in a supine patient with pneumoperitoneum. Falciform ligament sign occurs when a large amount of free air in the abdomen outlines the falciform ligament.
Rigler sign
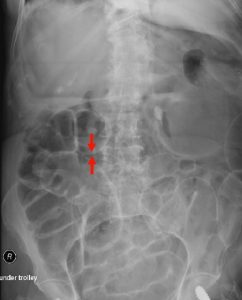
Figure 6. Abdominal X-ray showing Rigler sign in a supine patient with pneumoperitoneum. Rigler sign is seen when gas is present in both the intestinal lumen and the peritoneum, outlining both sides of the bowel wall (red arrows).
Football sign
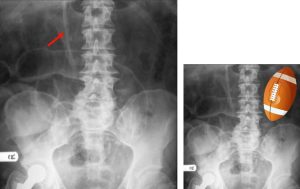
Figure 7. An abdominal x-ray showing football sign in a supine patient with massive pneumoperitoneum. Football sign is seen when large amounts of free air within the peritoneum result in a football-shaped region of radiolucency outlining the abdominal cavity. The falciform ligament may also be observed (red arrow) as a falciform ligament sign (see Figure 5) in representation of football sutures.
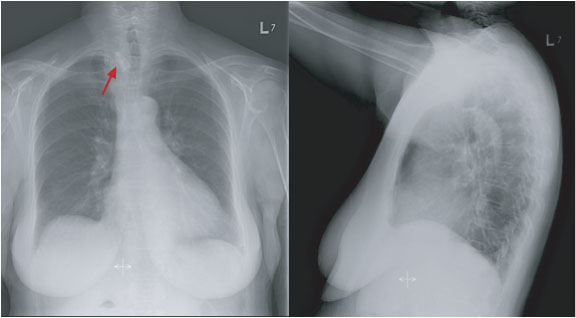
Subdiaphragmatic free air
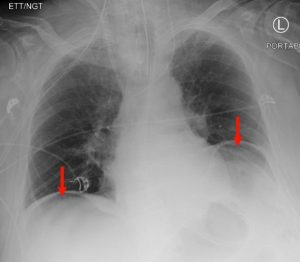
Figure 8. A chest x-ray showing subdiaphragmatic free air in an upright patient with pneumoperitoneum. Intraperitoneal free air is shown by crescents of lucency under the left and right hemidiaphragms (red arrows).
Other Locations of Extraluminal Gas
The four most common locations for extraluminal gas are:
- intraperitoneal (pneumoperitoneum, described above)
- retroperitoneal (pneumoretroperitoneum)
- in the bowel wall (pneumatosis intestinalis)
- within the liver (intrahepatic)
Pneumoretroperitoneum
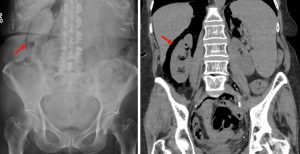
Figure 9. An abdominal x-ray (left) and coronal CT (right) demonstrating pneumoretroperitoneum in the presence of a sigmoid colon perforation. Air can be seen outlining the right kidney on both images (red arrows). Potential causes of pneumoretroperitoneum include a perforated retroperitoneal hollow organ and residual air from retroperitoneal surgery.
Pneumatosis Intestinalis
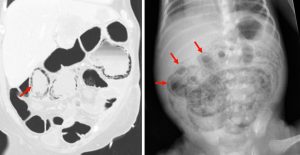
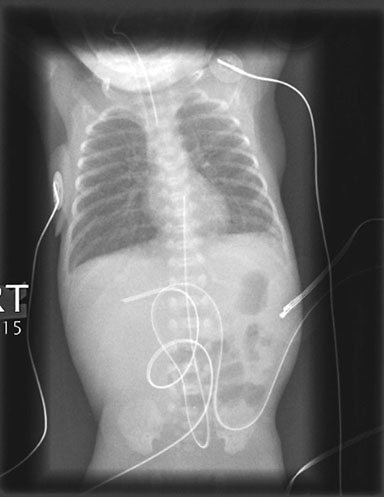
Figure 10. A coronal CT (left) demonstrating pneumatosis intestinalis–gas within the wall of the bowel, appearing as linear lucencies paralleling the contour of the adjacent bowel lumen (red arrows). Abdominal x-ray (right) in a pediatric patient with necrotizing enterocolitis demonstrating extensive pneumatosis intestinalis (red arrows). The most common cause of pneumatosis intestinalis is bowel ischemia in adults and necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants.
Intrahepatic Air
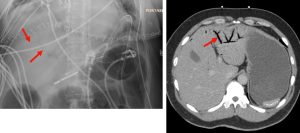
Figure 11. Abdominal x-ray (left) and axial CT (right) demonstrating intrahepatic portal venous gas, typically seen as branching air within the peripheral, small caliber vessels of the liver (red arrows). Important to distinguish from pneumobilia, the accumulation of air in the biliary tree which is often seen centrally in the liver. Potential causes of portal venous gas include ischemia, inflammation, trauma, and obstruction/dilation of the gastrointestinal tract and peritoneal cavity sepsis.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Questions
Question 1. A 68-year-old female with a history of H. pylori infection presents to the emergency department with tachycardia and sudden onset abdominal pain. An abdominal CT scan shows the following. Which finding is indicated by the arrow?
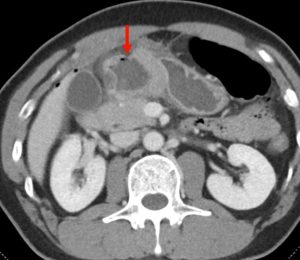
- Perforation
- Normal
- Gastric lipoma
- Free fluid
Answer: 1.
Explanation: This is an axial CT of the upper abdomen showing a clear discontinuity in the anterior gastric wall, which is likely to be the source of perforation (red arrow). A gastric lipoma is a rare lesion that can be definitively diagnosed on CT, and we would expect to see a homogeneous mass with a fat-density ranging between -70 and -120H for it to be diagnostic. Free fluid has a hypodense appearance on CT and we would expect it to look similar to the fluid found in the stomach or gallbladder.
Question 2. A 41-year of male presents to the emergency department with a 2-week history of RUQ pain. A CT scan shows the following. What is the next best step?
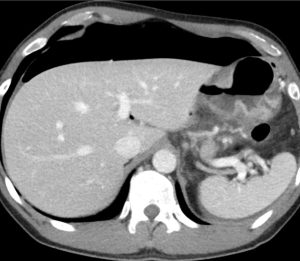
- Monitor the patient for 48hrs to ensure his condition improves
- Send the patient for endoscopy
- Prescribe a PPI and refer to a gastroenterologist
- Send the patient for emergency surgery
Answer: 4.
Explanation: The CT shows a gastric ulcer perforation and a large volume pneumoperitoneum. Immediate surgical intervention would be required to close the perforation. The etiology of the patient’s perforation is likely due to peptic ulcer disease, in which a referral to a gastroenterologist and PPI may be warranted. However, a perforated ulcer resulting in pneumoperitoneum would require prior urgent surgical intervention.
Question 3. A 52-year-old male presents to the emergency department with a 6-hour history of severe LUQ abdominal pain. On the physical exam, he is tachycardic and his abdomen is rigid. An abdominal x-ray shows the following. What sign observed on the x-ray is suggestive of pneumoperitoneum?
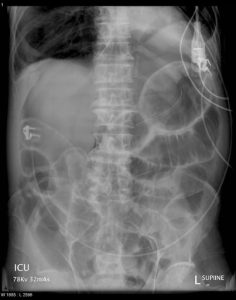
- Falciform ligament sign
- Rigler sign
- Football sign
- Subdiaphragmatic free air
Answer: 2.
Explanation: Rigler sign is observed where both sides of the bowel wall are well-defined due to the presence of free air both inside the bowel lumen and surrounding the bowel in the peritoneum. Falciform ligament sign, football sign, and subdiaphragmatic free air are not observed on this x-ray.
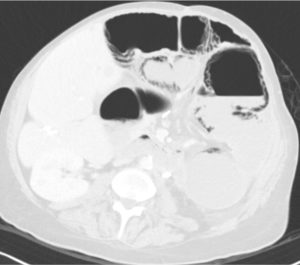
Question 4. A 74-year-old male presents to the emergency department with acute onset abdominal pain and distention, vomiting, and diarrhea. An abdominal CT scan shows the following. Which best describes the location of the extraluminal gas?
- Pneumoperitoneum
- Retroperitoneum
- Pneumatosis intestinalis
- Intrahepatic
Answer: 3.
Explanation: The extraluminal gas is located in the bowel wall, indicating pneumatosis intestinalis. Dark streaks of air can be seen following the contours of the bowel wall. There is no free air in the intraperitoneal (pneumoperitoneum) or retroperitoneal (pneumoretroperitoneum) spaces. There is also no free air observed in the liver (intrahepatic).
Question 5. What is the best imaging modality for a patient with a suspected gastrointestinal tract perforation?
- Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan
- Upright chest x-ray
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Abdominal x-ray
Answer: 1.
Explanation: Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT scan is the most sensitive and specific imaging modality for extraluminal gas indicative of a gastrointestinal tract perforation. Upright chest and abdominal x-rays are often performed first; however, they are less sensitive and specific for extraluminal gas than CT and are unable to localize the site of perforation. Ultrasound can detect extraluminal gas but is infrequently used for this purpose.
References
Alshahrani, M. A., Aloufi, F. F., Alabdulkarim, F. M., & Nadrah, A. H. (2017). The football sign. Abdominal Radiology, 42(11), 2769–2771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1177-5
Barros, M., Ferreira, L. A., Abreu, I., Caseiro, F., Coimbra, A. ;, & Pt, /. (2015). Abdominal extra-luminal gas-Is it always gastrointestinal perforation? Learning objectives. European Society of Radiology. https://doi.org/10.1594/ecr2015/C-2526
Chung, K. T., & Shelat, V. G. (2017). Perforated peptic ulcer - an update. World journal of gastrointestinal surgery, 9(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v9.i1.1
Ly, J. Q. (2003). The Rigler Sign. Radiology, 228(3), 706–707. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2283020302
Odom, S. R. (2021). Overview of gastrointestinal tract perforation. In M. Weiser, K. Raghavendran & W. Chen (Eds.), UptoDate. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-gastrointestinal-tract-perforation?sectionName=Presentations&topicRef=26&anchor=H73599335&source=see_link#H73599335
Sureka, B., Bansal, K., & Arora, A. (2015). Pneumoperitoneum: What to look for in a radiograph? Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, 4(3), 477. https://doi.org/10.4103/2249-4863.161369
Thompson, W. M., Kende, A. I., & Levy, A. D. (2003). Imaging characteristics of gastric lipomas in 16 adult and pediatric patients. American Journal of Roentgenology, 181(4), 981–985. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.181.4.1810981
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Glioblastoma
Marc Anthony Manzo, Nykan Mirchi, Dr. Kieran Murphy
Introduction
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common neoplasm found within adult brains, originating from glial cells. GBMs are often sporadic and carry a poor prognosis (median survival 12-18 months) as they are typically aggressive in nature and treatment-resistant. Incidence of GBM peaks between the ages of 65 and 75, with a slightly higher prevalence in males (3:2=M:F).
Patient presentation is often dictated by the location of the GBM in the brain as different brain functions may be affected depending on the brain region. For example, a tumour in the central sulcus may cause weakness while one in the parieto-occipital sulcus may impair vision. Survival is also strongly dependent on location as superficial tumours in the cerebrum may be more easily surgically removed. Less surgically-accessible tumours on the other hand may only be partially removed or not at all, thereby leading to a much lower survival rate.
GBMs tend to be large in size by the time a patient presents to clinic. Histopathology and molecular testing are essential for accurate diagnosis and prognostication, and can be done at the time of surgery or through a separate biopsy. Standard treatment may involve several modalities including surgery, chemo/radiotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy is a rapidly developing therapeutic modality, and includes developments such as personalized tumour vaccines [7, 8]. Personalized tumour vaccines require whole-exome sequencing of an individual’s tumour and comparing it to those of normal cells to identify antigenic epitopes of the cancerous cells. The sequences of these antigenic epitopes are then used to create a vaccine. Ultimately, the vaccine triggers the production of T-cells that can recognize the antigenic epitope that was sequenced, allowing the immune system to selectively invade and destroy the patient’s GBM. A single vaccine can contain up to 20 different targeting antigens.The challenge now is to generate an immune response that is long-lasting and strong enough to have a positive effect on a patient’s overall survival.
One important approach to strengthen the antitumor immune response is through the use of checkpoint inhibitors. Tumours take advantage of checkpoints to avoid T-cell mediated death. An example of such is PD-1 signalling. PD-1 receptors are expressed by T-cells. When the PD-1 receptor binds to its ligand, T-cell mediated apoptosis is inhibited. Tumour cells express PD-1 ligands to suppress T-cell responses via this mechanism. Thus, checkpoint inhibitors, which are monoclonal antibodies, work by disrupting the interaction of the PD-1 receptor (and other similar checkpoint proteins) and its ligand, allowing the T-cell to destroy the tumour cell..
Other medications, such as dexamethasone (DEX), can be administered pre- and/or postoperatively to reduce peritumoral edema and associated cognitive impairment [4]. It is important to note that DEX administration will reduce tumour enhancement on imaging [5]. This phenomenon of reduced enhancement is also seen with Avastin (Bevacizumab). Avastin mitigates peritumoral edema and reduces tumour enhancement on imaging similar to DEX [6]. This reduction in enhancement seen with Dex and Avastin administration is troublesome because it may be falsely interpreted as tumour regression, when in fact, the tumour may be unaltered or even progressing. This phenomenon is known as the pseudoresponse, and should always be taken into account when examining images from patients receiving DEX or Avastin.
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is an opportunistic infection that may occur in patients with prolonged steroid use, including DEX, due to their immunosuppressive effects. Although there are no strict guidelines on when to begin PCP prophylaxis in these patients, the American Thoracic Society recommends considering prophylaxis when taking >20mg/day of prednisone for over 1 month. [10] Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX) is the recommended prophylactic agent of choice for any patient without HIV. [10]
Brain tumour patients undergoing neurosurgical interventions are in a latent hypercoagulable state and are therefore at a high risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). [11] Primary prevention is encouraged in these patients through the use of pneumatic compression stockings in addition to low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) or unfractionated subcutaneous heparin. [12] The treatments should be started pre-operatively and resumed 24-48hrs after surgery. As the risk of DVT remains high while the patient is immobile, treatments should be continued until they can ambulate.
Key radiographic features:
- CT: irregular thick margins. An irregular hypodense core signalling necrosis. Peripheral vasogenic edema and intense irregular enhancement of margins.
- MRI
- T1: iso-to-hypointense, central heterogeneous signal.
- T1 contrast (Gd): peripheral enhancement (irregular/nodular) around a necrotic core.
- T2/FLAIR: Hyperintense with surrounding vasogenic edema.
Clinical case
Patient J.L. is a 58 year-old male that has been hospitalized after experiencing a generalized seizure. The patient was stabilized and treated with anti-seizure medication. On history, patient J.L.’s spouse noted that he had been experiencing headaches and nausea for the past month. J.L. also experienced alterations in mental capacity, specifically being more forgetful during the past month.
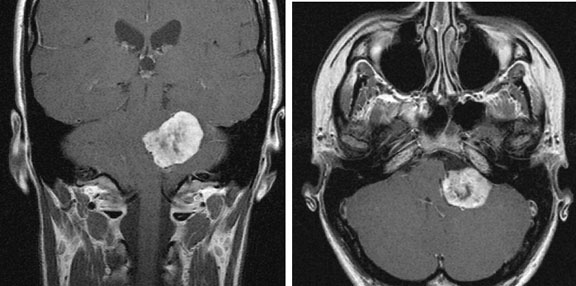
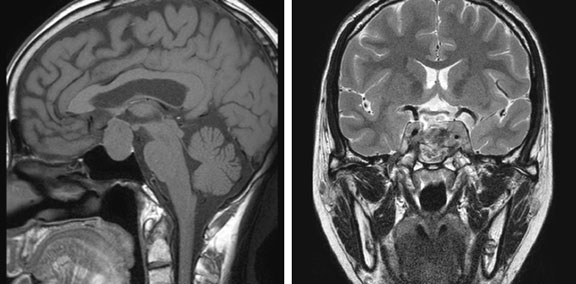
The patient underwent an MRI scan and the following images were obtained.
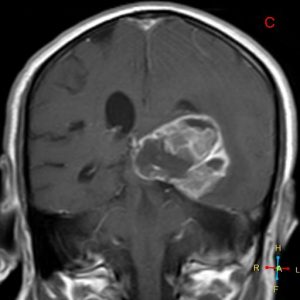
Figure 1. Axial T1
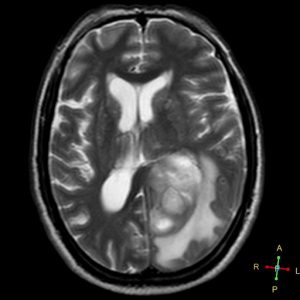
Figure 2. Axial T2
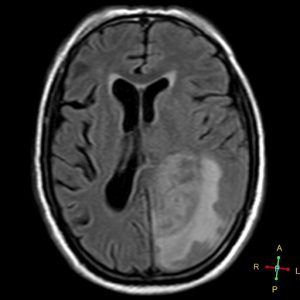
Figure 3. Axial FLAIR
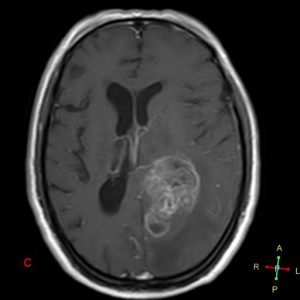
Figure 4. Axial T1 + Gadolinium

Figure 5. Coronal T1 + Gadolinium
Patient J.L was referred to neurosurgery for maximal resection of the tumour. Diagnosis of GBM was confirmed in surgery via histological and molecular testing. Treatment also included adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy (temozolomide). Despite undergoing an intense treatment regimen, prognosis for patient J.L. remains grim. Median survival for patients diagnosed with GBM is less than 2 years.
On postoperative day 3, patient J.L. underwent contrast-enhanced MRI to determine the extent of tumour resection. No residual tumour was detected upon imaging. Patient J.L. was scheduled for follow-up imaging every 12 weeks, as GBM tends to be a highly recurrent disease with the median time to recurrence being approximately 7 months (even with standard therapeutic regimens). Recurrence of patient J.L.’s tumour was detected at 17 months post-surgery. Given his age and health, J.L. was scheduled for a second surgery to resect the tumour. Repeat surgeries have been shown to have a positive effect on overall survival [9].
Questions:
- Describe the features and anatomical location of the lesion imaged. (short answer)
- “Irregular shaped ill-defined intra-axial space occupying lesion involving the inferior aspect of left temporo-occipital region, exhibits heterogeneous enhancement in post contrast study and exerting a positive mass effect upon the temporal horn of left lateral ventricle. Multiple areas of intralesional necrosis are noted.”
- Given this patient’s initial presentation and imaging, what else is on your differential diagnosis? (short answer)
- Cerebral metastasis, primary CNS lymphoma, cerebral abscess, tumefactive demyelination, and cerebral infarction.
- What radiographic features would you expect to see on a T1 scan with contrast of a GBM?
- Peripheral/nodular enhancement of the tumour.
- Homogeneous enhancement of the tumour.
- Enhancement of necrotic core.
- Non-enhancing margins
Answer: 1
- What might the nonhomogeneous enhancement of GBM in T1 + contrast be caused by? (select all that apply)
- Necrosis
- Hemorrhage
- Demyelination
- Ischemia
Answer: 1 and 2
- List at least 3 poor prognostic factors of GBM? (short answer)
- Greater degree of necrosis and enhancement, older age, deeper location of the tumour, and lower pre-diagnostic functional status.
- Which of the following features may be indicative of vasogenic edema surrounding a space occupying lesion in the brain? (select all that apply)
- Hyperintense region on T2
- Hyperintense region on T1 + contrast
- Loss of grey/white matter differentiation
- Accentuation of grey-white differentiation
- Sulcal effacement
Answer: 1, 4, 5
- What is the recommended timeline for follow-up for this patient?
- 1-2 days after surgery and 1-2 months thereafter.
- 7-14 days after surgery and 1-2 months thereafter.
- 1-2 days after surgery and 6-8 months thereafter.
- 7-14 days after surgery and 6-8 months thereafter.
Answer: 1
- Which brain region is most commonly affected by GBM?
- Cerebral cortex
- Cranial nerves
- Brainstem
- Cerebellum
- Deep brain nuclei
Answer: 1
Sources
- Gaillard F. Glioblastoma: Radiology Reference Article [Internet]. Radiopaedia Blog RSS. [cited 2021Jul23]. Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/glioblastoma
- Jeffrey N Bruce MD. [Internet]. Glioblastoma Multiforme Clinical Presentation: History, Physical Examination. Medscape; 2021 [cited 2021Jul23]. Available from: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/283252-clinical
- Clinical presentation, diagnosis, and initial surgical management of high-grade gliomas [Internet]. UpToDate. [cited 2021Jul23]. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-presentation-diagnosis-and-initial-surgical-management-of-high-grade-gliomas
- Cenciarini M, Valentino M, Belia S, Sforna L, Rosa P, Ronchetti S, et al. Dexamethasone in Glioblastoma Multiforme Therapy: Mechanisms and Controversies. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience. 2019;12.
- Dietrich J, Rao K, Pastorino S, Kesari S. Corticosteroids in brain cancer patients: benefits and pitfalls. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology. 2011;4(2):233–42.
- Gaillard F. Glioblastoma with pseudoresponse: Radiology Case [Internet]. Radiopaedia Blog RSS. [cited 2021Jul23]. Available from: https://radiopaedia.org/cases/glioblastoma-with-pseudoresponse?lang=us
- Huang B, Li X, Li Y, Zhang J, Zong Z, Zhang H. Current Immunotherapies for Glioblastoma Multiforme. Frontiers in Immunology. 2021;11.
- Baratta MG. Glioblastoma is ‘hot’ for personalized vaccines. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2019;19(3):129.
- Lu VM, Jue TR, McDonald KL, Rovin RA. The Survival Effect of Repeat Surgery at Glioblastoma Recurrence and its Trend: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurgery. 2018;115.
- Limper AH, Knox KS, Sarosi GA, Ampel NM, Bennett JE, Catanzaro A, et al. An official American Thoracic Society Statement: Treatment of fungal infections in ADULT pulmonary and critical care patients. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2011;183(1):96–128.
- Collen JF, Jackson JL, Shorr AF, Moores LK. Prevention of venous thromboembolism in neurosurgery. Chest. 2008;134(2):237–49.
- Khan NR, Patel PG, Sharpe JP, Lee SL, Sorenson J. Chemical venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in neurosurgical patients: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2018;129(4):906–15.
Images: Case courtesy of Dr Ahmed Abdrabou, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 22779
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Intracranial Hemorrhage
Jason Chung, Natalie Kozlowski, Kristiana Xhima, Dr. Kieran Murphy, Dr. Mehran Nasralla
Presentation
A 26-year-old male patient, Mr. C.K., presents to the emergency department. Four hours ago, he was struck in the head by a golf ball while golfing with his friends. In the emergency department, the patient appears intoxicated and incoherently mutters. He complains of a worsening headache, nausea and vomiting. A collateral history from his friends reveals that he was in moderate pain but did not lose consciousness immediately following the accident. Subsequently, his symptoms and level of consciousness however subsequently deteriorated two hours after the accident. Mr. C.K. regularly consumes alcohol and electronic cigarettes; on weekends, he recreationally uses cocaine. No other significant past medical history present.
Physical Examination
Mr. C.K. was examined in the emergency department by the triage nurse.
Vital signs: BP: 160/110. RR: 24. Temp: 37.7C. Heart rate: 45 BPM
The patient was dyspneic at rest.
Ipsilateral dilation of the left pupil.
Swelling and erythema in the left posterior aspect of the head. No scalp lacerations.
He is graded a 8 on the Glasgow Coma Scale.
A neurological examination could not be conducted due Mr. C.K.’s worsening level of consciousness.
Laboratory testing
Complete blood count indicates that Mr. C.K. is anemic with no evidence of thrombocytopenia. Coagulation studies (PTT, PT/INR) are unremarkable. No abnormalities in serum electrolytes or liver function markers are observed.
Imaging
The patient is immediately taken for a non-contrast CT Head, to identify a cause and potential management strategies.
Findings: An axial plane CT demonstrates a hyperdense biconvex or lens-shaped collection over the left frontoparietal cerebral convexity. On axial images, the haematoma had a depth of 5 cm in the transverse dimension and length of 12 cm in the anteroposterior dimension. Although predominantly hyperdense, the collection contained a low-density region centrally. No crossing of suture lines.
Features of mass effect included generalised sulcal effacement, 6 cm rightward midline shift, subfalcine herniation and lateral ventricular effacement.
No contrecoup injury present.
Bone windows demonstrated an undisplaced fracture of the left side of the frontal bone extending inferiorly across the pterion.
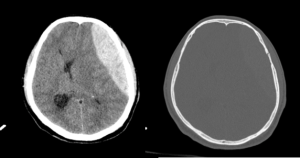
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Practice Questions
Question 1. Which blood vessel is most commonly ruptured in an epidural hematoma (EDH)?
- Superficial temporal arteries
- Middle meningeal artery
- Superior anastomotic vein
- Deep temporal arteries
Answer: 2. Middle meningeal artery. EDH is most commonly (~85%) due to arterial injury. The middle meningeal artery is the most common culprit, as it courses in the anterior and middle cranial fossa. There is a large association with cranial fractures.
Question 2. Which of the following medications should a patient with suspected epidural hematoma immediately discontinue?
- Acetaminophen
- Warfarin
- Ramipril
- Furosemide
Answer: 2. Warfarin. Patients on anticoagulants are at risk of hematoma enlargement and are indicated for reversal anticoagulants when surgical intervention is required. Anticoagulation reversal for patients managed nonoperatively is also common. The risks and benefit of anticoagulation reversal should be carefully considered for each patient.
Question 3. On non-contrast CT of the brain, acute intracranial hemorrhage is:
- Hypodense to fat
- Hyperdense to bone
- Hyperdense to brain parenchyma
- Indistinguishable from CSF
Answer: Hyperdense to brain parenchyma. CT is the gold standard to assess patients with suspected intracranial hemorrhage in the acute setting. CT is the most used imaging modality in the initial workup of patients with suspected intracranial pathology. Its advantages include its ubiquity, positive safety profile (and lack of contraindications and safety concerns as with MR) and relative low expense. There are five main x-ray densities – bone, soft tissue (brain), water (CSF), fat, and air - which can also be applied to CT interpretation where they are defined by a range of density units (Hounsfield Units; HU). Acute haematoma (50-90 HU) appears denser than brain (25-35 HU) but less than bone (>300) on CT. CT is sensitive for the detection of small amounts of acute blood products which appear hyperdense relative to brain parenchyma.
Question 4. An enlarging epidural hematoma will result in elevation of intracranial pressure. In a clinical setting, the Cushing Triad suggests elevated ICP, which is:
a. Elevated blood pressure
b. Ipsilateral pupil dilation
c. Bradycardia
d. Focal neurological symptoms
e. Confusion
f. Respiratory depression
g. Hemiparesis
- a,c,e
- b,f,g
- d,e,g
- a,c,f
Answer: 4 (a,c,f). Cushing Triad is identified by bradycardia, respiratory depression and hypertension. This finding may indicate the need for immediate intracranial intervention to prevent CNS depression and death.
Question 5. A 9-year-old child is brought to the ED following cranial trauma after falling off their bicycle. The child was drowsy immediately following the trauma but is currently alert and communicative (GCS 15). The CT head demonstrates an acute epidural haematoma over the right temporal convexity. Which sign on the following axial CT image is most prognostically significant?
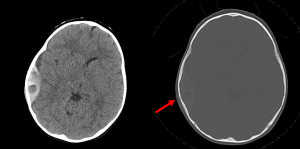
- Locoregional sulcal effacement midline shift
- Haematoma depth and location
- Rounded hypodensity within the clot
- Skull fracture
- Ventricular compression
Answer: 3. Hypodensity within the clot. Clotted blood in epidural haematomas is hyperdense. The hypodense regions within the clot represent hyperacute unclotted blood, commonly referred to as the Swirl Sign, and indicates active extravasation of blood. The swirl sign is an independent predictor of haematoma expansion and poor outcome. This is particularly pertinent in this case whereby an alert patient with a relatively modest clot on imaging may falsely reassure a clinician, when instead the clot is actively expanding in a patient experiencing a lucid interval prior to eventual decompensation from progressing mass effect. The swirl sign may help predict haematoma expansion and thus identify patients who will benefit from surgical management.
Ischemic Stroke
Kesikan Sabapathy Jayaraj, James Sanayei, Dr. Kieran Murphy
ID: Mrs. Jane Doe, 67-year-old female
Case presentation:
Mrs. Doe was found on her kitchen floor by her son at 8:00 AM this morning. He immediately called 911, and EMS arrived by 8:15 AM. They found that Mrs. Doe was conscious but unable to communicate. Her vital signs were within normal limits, though her pulse was irregular. Suspecting a possible stroke, EMS called ahead to the nearest stroke centre, and a “Code Stroke” was initiated. Mrs. Doe arrived at Toronto Western Hospital at 8:35 AM, and a team of neurologists was ready to evaluate her.
On arrival, Mrs. Doe displayed right-sided hemiparesis, facial droop, hemisensory impairment, and homonymous hemianopia, as well as global aphasia. Her gaze was deviated to the left. Her son noted that she had appeared normal when he last saw her the night before, at roughly 10:00 PM. Her NIH Stroke Score was > 20.
Differential diagnosis:
Some of the following conditions were considered: ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, seizure, head trauma, neoplasm, complex migraine, and AVM. An ECG study confirmed the presence of atrial fibrillation. Due to the clinical presentation, middle cerebral artery stroke (MCA) stroke resulting from a cardiac embolism was considered the most likely pathology. Urgent imaging studies were ordered to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate potential treatment options. Due to the acute presentation, CT imaging was selected over MRI.
Imaging:
CT head without contrast:
Brain parenchyma: No acute hemorrhage. No mass effect or herniation. Gray-white differentiation is maintained. Hyperdense MCA sign in M1 segment of left MCA.
Ventricles/extra-axial spaces: No hydrocephalus or extra-axial fluid collections. Normal bones and soft tissues. Visualized paranasal sinuses and mastoids are clear.
Other: Visualized lung apices are clear. No neck mass or suspicious lymph nodes. Bones demonstrate no significant abnormality.
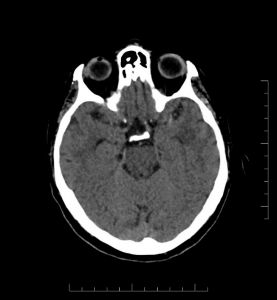
Figure 1: Axial head CT image without contrast showing hyperdense MCA sign.
CTA Head:
Complete occlusion of the M1 segment of the left MCA. No aneurysm.
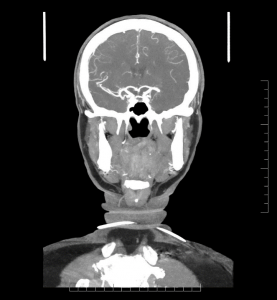
Figure 2: Coronal CT angiography image of the cerebral arteries showing a complete occlusion of the left MCA.
CTA Neck:
Great vessels: Visualized segments are patent.
Internal carotid arteries: Mild stenosis (<50%) bilaterally by NASCET criteria at the carotid bifurcation. Not hemodynamically significant. No dissection.
Vertebral arteries: Patent extracranial segments. No dissection.
CT Perfusion:
Total hypoperfusion: Using the threshold of Tmax >6 seconds, there is an area of hypoperfusion in the left MCA territory with a total volume of 92 ml.
Infarct core: Using the threshold of CBF <30%, there is an infarct core in the left MCA territory with a total volume of 21 ml.
Penumbra: The penumbra volume is 71 ml. The mismatch ratio is 4.38.
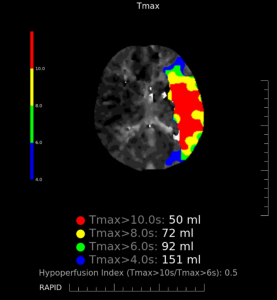
Figure 3: CT perfusion map showing areas of hypoperfusion in the left MCA territory as defined by different Tmax thresholds.
Impression:
Complete occlusion of the M1 segment of the left MCA. Infarct present in left MCA territory with significant tissue at risk (infarct core volume of 21 ml, penumbra volume of 71 ml).
Treatment:
Because of the significant time since Mrs. Doe was last seen normal, tPA was not administered. Mrs. Doe was taken to the angiography suite and underwent endovascular thrombectomy, which was successful.
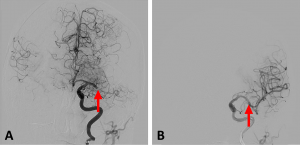
Figure 4: AP cerebral angiography images showing (A) a complete blockage of the left MCA (arrow) and (B) restoration of blood flow following endovascular thrombectomy.
Outcome and follow up:
Repeat CT scan 48 hours later showed no signs of mass effect, hemorrhagic transformation, or hydrocephalus. Mrs. Doe was started on ASA (162 mg OD), then switched to dabigatran (150 mg BID) after two weeks. She was also referred to a cardiologist for ongoing assessment and treatment of her atrial fibrillation.
Follow-up Questions:
- If an acute stroke is suspected, which imaging protocol is used to identify if the patient is a candidate for IV thrombolytic therapy or endovascular thrombectomy (EVT)?
- CT head without contrast + CT angiography (CTA) of the neck arteries and the circle of Willis + CT perfusion scan (CTP)
- MRI head without contrast + MR angiography (MRA) of the neck arteries and the circle of Willis
- CT head with contrast and skull X-ray
- Carotid angiography
Answer: 1
Explanation: If an acute stroke is suspected, a rapid and informative imaging examination is required to determine whether a patient is a candidate for therapy.[1] While MRI is considered the gold standard for stroke diagnosis, CT scans can be performed more quickly than MRI scans, making them more useful in an emergency setting.[1,2] Answer A shows the standard CT protocol used in most regional stroke centres that accept “code strokes”. CT head without contrast helps to rule out hemorrhages, established infarcts, and pathologies that may mimic stroke.[1,2] CTA is used to confirm arterial occlusion, supporting the diagnosis of ischemic stroke and localizing the occlusion to evaluate the use of EVT.[2] CTP may also be acquired in the emergency setting to evaluate for territorial changes in cerebral blood flow suggestive of stroke. It is particularly valuable for identifying core infarct and salvageable ischemic penumbra and is becoming an important part of interventional decision making.[2]
- Which of the following is NOT a role of CT head without contrast in acute stroke?
- To rule out an established infarct
- To rule out an acute hemorrhage
- To rule out other mimicking pathologies that may present like a stroke
- To confirm an arterial occlusion
Answer: 4
Explanation: A noncontrast head CT is used to rule out an established infarct or intracerebral hemorrhage that would contraindicate interventions such as IV tPA.[2] It can also help rule out lesions that might mimic acute ischemic stroke, such as tumors.[3] Thus, only answer D is not a role of CT head without contrast in the assessment of suspected acute stroke. Although the presence of hyperdense artery sign on CT is highly specific for an occlusion, it is not very sensitive, as many occlusive thrombi are not large or dense enough to be detected.[4] One of the most accurate means of localizing an occlusive thrombus is computed tomography angiography (CTA), which is why this modality is typically included in a stroke workup. In addition to locating the occlusion, CTA can also be used to measure clot length, grade collateral blood flow, and detect arterial dissection.[4]
- If an MRI scan was performed on a patient who suffered a stroke 1 week ago, which of the following findings might be seen?
- DWI – high intensity, T2 FLAIR – low intensity
- DWI – low intensity, T2 FLAIR – high intensity
- DWI – normal, T2 FLAIR – normal
- DWI – high intensity, T2 FLAIR – high intensity
Answer: 4
Explanation: In ischemic stroke, DWI sequences will show high signal intensity almost immediately, which usually persists for 10-14 days. After that point, the DWI signal may be variable.[5] FLAIR sequences will show high signal intensity starting from the late hyperacute stage (6-24 hours). The signal intensity usually remains high until the chronic stage (>3 weeks).[5]
- In a patient with homonymous hemianopsia, we might expect a CTA scan to show an occlusion of which of the following arteries:
- Contralateral ACA
- Contralateral PCA
- Ipsilateral MCA
- Ipsilateral basilar artery
Answer: 2
Explanation: Homonymous hemianopsia (HH) is a visual defect characterized by the loss of the same side of the visual field in both eyes.[6] It is common following a stroke, with as many as 10% of stroke patients suffering from permanent HH.[6] It results from damage to the retrochiasmal visual tract (occipital lobe or optic radiations) on the side contralateral to the visual field loss.[6,7] Therefore, in patients with HH, ischemic stroke of the contralateral MCA or PCA should be suspected.
- Malignant MCA infarction is a term used to describe a significant infarction of the MCA causing space occupying cerebral edema and rapid neurological deterioration. Which of the following agents would be most helpful in treating this condition?
- Dexamethasone
- 9% saline
- Mannitol
- Fosphenytoin
Answer: 3
Explanation: Osmotic therapy is rapid and effective medical intervention for lowering intracranial pressure (ICP). Osmotic agents, such as mannitol or hypertonic saline, work primarily by drawing water out of the brain parenchyma and into the intravascular compartment, decreasing brain volume and ICP.[8] Mannitol also acts as a diuretic: by increasing the osmotic pressure of glomerular filtrate, it decreases reabsorption of water and electrolytes and increases urinary output.[8] Finally, it is thought to also reduce ICP by decreasing blood viscosity, which leads to a transient increase in cerebral blood flow. This increase in blood flow causes vasoconstriction, leading to reduced ICP.[8]
References
[1] Fox AJ, Symons SP, Howard P, Yeung R, Aviv RI. Acute stroke imaging: CT with CT angiography and CT perfusion before management decisions. Am J Neuroradiol 2012;33:792–4. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3099.
[2] Lin MP, Liebeskind DS. Imaging of Ischemic Stroke. Contin (Minneap Minn) 2016;22:1399–423. https://doi.org/10.1212/CON.0000000000000376.
[3] Birenbaum D, Bancroft LW, Felsberg GJ. Imaging in acute stroke. West J Emerg Med 2011;12:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1093/med/9780199582808.003.008.
[4] Gasparian GG, Sanossian N, Shiroishi MS, Liebeskind DS. Imaging of occlusive thrombi in acute ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke 2015;10:298–305. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijs.12435.
[5] Allen LM, Hasso AN, Handwerker J, Farid H. Sequence-specific MR imaging findings that are useful in dating ischemic stroke. Radiographics 2012;32:1285–97. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.325115760.
[6] Goodwin D. Homonymous hemianopia: Challenges and solutions. Clin Ophthalmol 2014;8:1919–27. https://doi.org/10.2147/OPTH.S59452.
[7] Zhang X, Kedar S, Lynn MJ, Newman NJ, Biousse V. Homonymous hemianopia in stroke. J Neuro-Ophthalmology 2006;26:180–3. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wno.0000235587.41040.39.
[8] Hinson HE, Stein D, Sheth KN. Hypertonic saline and mannitol therapy in critical care neurology. J Intensive Care Med 2013;28:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066611400688.
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Osteomyelitis
Kalter Hali, Brian Tsang, Dr. Angela Atinga
Introduction
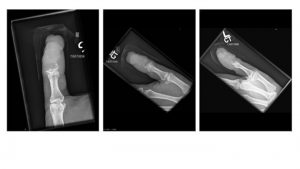
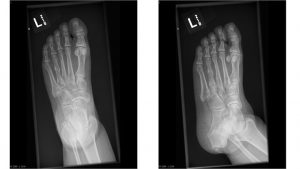
A.B. is a 58-year-old male with type II diabetes presenting to the ER with swelling and pain in his right middle finger. The pain and swelling started ten days earlier, caused by an accidental injury to his right middle finger while pruning the garden. He immediately went to the ER, and the emergency doctor at that time ordered an X-ray (see X-ray at initial visit) and determined no bone fracture. His wound was cleaned and bandaged. Tetanus prophylaxis was given, and he was instructed to take Tylenol as needed for pain. Currently, A.B. tells you that his pain has been worsening over the past ten days and that he is concerned because “it's not getting any better”. You observe that his finger is visibly swollen and red. You determined that the swollen finger is warm, tender and has a significantly reduced range of motion. At this point, you decide to take his vitals and X-ray his hand.
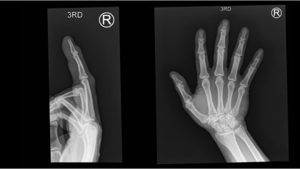
Figure 1. X-rays at initial visit (10 days earlier)
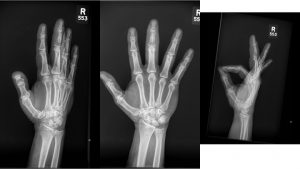
Figure 2. X-rays at current visit
- How would you describe the X-ray images?
X-Rays at initial visit (10 days earlier)
- Slight soft tissue swelling of the right middle finger
- No fracture present
X-Rays at current visit
- Marked soft tissue swelling of right middle finger
- The distal interphalangeal joint (DIP) space of the right middle finger is narrowed and less distinct compared to adjacent DIP joints.
- Mixed lucency of the middle phalanx, cortical disruption and periosteal reaction
Review Questions
What is your working diagnosis and differential diagnosis?
- Osteomyelitis
- Septic arthritis
- Cellulitis
- Charcot joint
- Osteosarcoma
- Metastasis
- Arthritis
What additional diagnostic tests will you consider in this case?
- CBC to look for signs of infection
- Blood culture to look for any microorganisms
- MRI can be done if still unsure from the results of the x-rays and blood cultures
- Ultrasound to assess the surrounding soft tissues
- Bone biopsy
What are the option treatments for osteomyelitis?
- Surgical debridement of the area
- Targeted antibiotics
What is the most common bacteria that causes osteomyelitis?
- Staphylococcus aureus [1]
What are the four features of aggressive bone lesions?
- Cortical or bone destruction
- Periosteal reaction
- Poor zone of transition (i.e. poorly defined)
- Soft tissue mass.
Additional Images
Metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma
Lung cancer metastasis
Melanoma
Breast cancer metastasis
References
[1] Schmitt SK. Osteomyelitis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2017 Jun;31(2):325-338. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2017.01.010.
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Pneumonia: A Radiology Case Report
Jeffrey Lam Shin Cheung, Dr. Anastasia Oikonomou
Presentation
John is a 43-year-old male coming to the emergency department for 4 days of fever and shortness of breath. He believes that he also started to have a productive cough and pleuritic chest pain about 3 days ago. He denies any blood in his sputum or recent trauma. He has felt tired in the last week and denies any unintentional weight changes in the last year. His remaining review of systems is unremarkable.
On past medical history, he has no prior diagnoses, and he has no prescription medications.
On social history, he was born and raised in Canada. He denies any recent travel or having any recent contacts with sick individuals, though he mentions that he attended a large wedding the week prior. He’s employed as an office worker and currently smokes with a 10-packyear history. He drinks 2 glasses of wine per week and denies any recreational drug use.
Physical Exam
His vitals are as follows: T38.7oC; HR98; RR21; BP 134/87 mmHg; O2 saturation 96% on room air.
On exam, he appears tired but in no acute distress. His respiratory exam is notable for dullness on percussion and crackles heard in the right lower lung zone. His left lung is clear. Cardiac and abdominal exams are unremarkable.
Imaging and Investigations
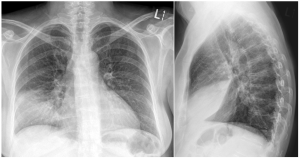
A CBC is ordered and demonstrates leukocytosis with a WBC of 14.2 × 109/L. A sputum sample is obtained in the emergency department and sent for gram stain and culture and sensitivity. A chest x-ray is also ordered with images shown below (Figure 1).
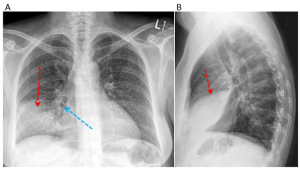
Figure 1. Anteroposterior (A) and lateral views (B) at the time of presentation. The left lung is normal. There is consolidation in the right anterior and inferior aspect of the right lung (red arrow) with air bronchograms (blue arrow) shown. Do you know which lung lobe is affected? Please see question 2 below for the answer.
Case resolution
The chest radiograph confirms that he has pneumonia. The sputum culture grows gram-positive diplococci bacteria that are confirmed to be Streptococcus Pneumoniae. Sensitivity analysis shows that the bacteria is susceptible to Ceftriaxone, and John is subsequently started on a 7-day course of Ceftriaxone 2 grams IV once daily. He improves by the end of the treatment course and is discharged home.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Bonus: COVID-19 pneumonia
X-ray findings vary widely (1). Several examples are provided below in Figure 2.
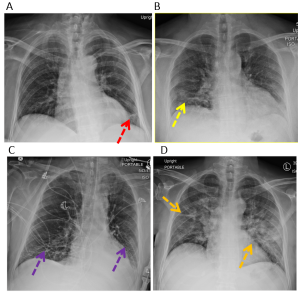
Figure 2. Examples of COVID-19 lung infection. (A) Reticular opacities in the left lower lung zone (red arrow). (B) Patchy bilateral peripheral ground glass opacities (yellow arrows). (C) Patchy bilateral lower lung zone ground glass opacities (purple arrows). (D) Bilateral diffuse consolidative opacities in the mid and lower lung zones (orange arrows).
On CT imaging, COVID-19 infection typically shows bilateral peripheral ground glass opacities, often with a lower lung predominance (1). An example is provided in Figure 3.
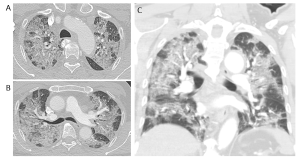
Figure 3. COVID-19 lung infection on CT. (A) and (B) axial reconstruction at the level of the upper and mid lung zones and (C) coronal reconstruction. There are extensive patchy bilateral ground glass opacities with no definite lung zone predominance.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Practice Questions
Question 1. Which of the following is considered the gold standard for diagnosing pneumonia?
- Clinical exam
- Chest radiograph
- Sputum culture
- Complete blood count (CBC)
Answer: 2
Explanation: A thorough clinical history and exam are helpful for pointing towards pneumonia, but a chest radiograph is typically considered the gold standard and required for making a diagnosis. A CBC showing leukocytosis suggests infection, but this is not specific for pneumonia. Likewise, a positive sputum culture is non-specific and may be due to an upper airway infection or represent a false positive result (2).
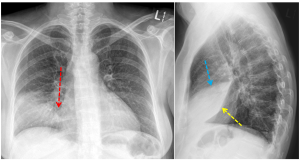
Question 2. A 43-year-old male presents for 4 days of cough and fever. His chest radiograph is shown below. Which lung lobe has the area of consolidation?
- Right upper lobe
- Middle lobe
- Right lower lobe
- Lingula
Answer: 2
Explanation: Using the silhouette sign (3), one can determine which lobe has the area of consolidation.
In this case, the consolidation obscures the right heart border (red arrow) indicating that the right middle lobe is affected. This is confirmed with the lateral chest radiograph, which shows that the area of consolidation is bordered by the major fissure inferiorly (oblique fissure, yellow arrow) and by the minor fissure superiorly (horizontal fissure, blue arrow).
In typical cases:
- consolidation in the right lower lobe would obscure the right hemidiaphragm.
- consolidation in the left lower lobe would obscure the left hemidiaphragm.
- consolidation in the lingula would obscure the left heart border.
Question 3. A 69-year-old male presents at the Emergency Department for 3 days of cough, fever, and confusion. He has a respiratory rate of 32 and a blood pressure of 88/55 mmHg. There is dullness on percussion, and crackles are heard bilaterally. Investigations show a WBC of 13.6 × 109/L and a BUN of 7.3 mmol/L. His chest radiograph is shown below. What would be the best next step in management?
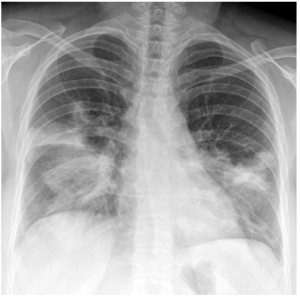
- Watchful waiting
- Diagnostic thoracentesis
- Ceftriaxone and Azithromycin
- Combination of Rifampin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide, and Ethambutol
Answer: 3
Explanation: This patient’s presentation and radiograph are suspicious for multifocal pneumonia. He also has a CURB-65 score of 5 indicating that he should be treated with a third-generation cephalosporin and Azithromycin IV (4).
A thoracentesis could be considered for a pleural effusion in which case, his chest radiograph would likely show blunting of the costophrenic angles and a meniscus sign. See examples of pleural effusions here
The RIPE (Rifampin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide, and Ethambutol) medications would be appropriate for treating tuberculosis. Although there are areas of consolidation in this patient’s chest radiograph, it lacks other more specific findings that would point toward tuberculosis such as lymphadenopathy, pleural effusions, cavitary lesions, or miliary nodules. Reactivation tuberculosis also usually predominates in the apical and upper lung zones (5).
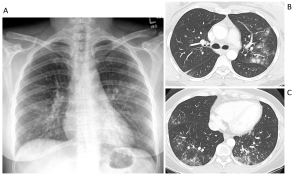
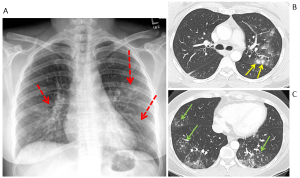
Question 4. It is December. A 52-year-old female presents with pleuritic chest pain, fever, and dry cough over the last 4 days. She felt very unwell last night and vomited twice. Her chest radiograph and images from her CT scan are shown below. What medication treatment would you recommend?
- Oseltamivir
- Ceftriaxone
- Ventolin
- Nintedanib
Answer: 1
Explanation: This patient had influenza, which can be managed with antiviral medication. Her chest radiograph shows bilateral patchy ill-defined micronodular opacities with bronchograms (red arrows). Her CT scan confirms the presence of ill-defined peribronchial nodules with surrounding ground glass opacity in the left upper lobe (yellow arrows) and clusters of centrilobular and branching micronodules (tree-in-bud pattern) in the middle and bilateral lower lobes (green arrows). (6)
Ventolin is typically considered for managing acute exacerbations of obstructive lung diseases such as asthma and COPD. These conditions should be diagnosed with objective pulmonary function testing and not with radiographic imaging.
Nintedanib and Pirfenidone are used to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). IPF typically shows a basal predominant subpleural reticular pattern with traction bronchiectasis and/or honeycombing. Micronodules, consolidations, and ground-glass opacity point away from a diagnosis of IPF. See examples of IPF here.
References
- Kanne JP, Bai H, Bernheim A, Chung M, Haramati LB, Kallmes DF, Little BP, Rubin G, Sverzellati N. COVID-19 imaging: what we know now and what remains unknown. Radiology. 2021 Jun;299(3):E262-79.
- Htun TP, Sun Y, Chua HL, Pang J. Clinical features for diagnosis of pneumonia among adults in primary care setting: a systematic and meta-review. Scientific reports. 2019 May 20;9(1):1-0.
- Longuet R, Phelan J, Tanous H, Bushong S. Criteria of the silhouette sign. Radiology. 1977 Mar;122(3):581-5.
- Rider AC, Frazee BW. Community-acquired pneumonia. Emergency Medicine Clinics. 2018 Nov 1;36(4):665-83.
- Nachiappan AC, Rahbar K, Shi X, Guy ES, Mortani Barbosa Jr EJ, Shroff GS, Ocazionez D, Schlesinger AE, Katz SI, Hammer MM. Pulmonary tuberculosis: role of radiology in diagnosis and management. Radiographics. 2017 Jan 1;37(1):52-72.
- Koo HJ, Lim S, Choe J, Choi SH, Sung H, Do KH. Radiographic and CT features of viral pneumonia. Radiographics. 2018 May 1;38(3):719-39.
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Oliver Chow, Ananya Srivastava, Dr. Angela Atinga
A 45-year-old woman presents to the clinic with pain in her hands. She has been employed as a seamstress for over 20 years and is concerned about how this will affect her work. She says she had flu-like symptoms last month, around the same time that she noticed the pain. Since then, she has been feeling fatigued, and complains of a slight fever. She is perimenopausal and is not currently on any medications. Her blood pressure was 110/75, her temperature was 39.7°C, and her heart rate was 82bpm. You decide to take x-rays of her hands, as seen below.
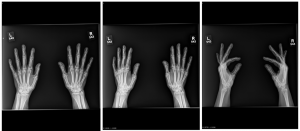
=What is not a part of the differential diagnosis?
-
- Joint manifestation of psoriasis
- Gout
- CPPD (Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Which one of the following is the greatest risk factor for being diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis?
- Family history of osteoarthritis
- Diagnosis of lupus
- Previous history of cancer
- Repeated use of hand joints at work
- Which joints are most likely to be affected if this is a case of rheumatoid arthritis?
- Metacarpophalangeal joints and radiocarpal joints
- Metacarpophalangeal joints and proximal interphalangeal joints
- Metacarpophalangeal joints and distal interphalangeal joints
- Radiocarpal joints and distal interphalangeal joints
What would you do next?
-
- Secondary imaging studies
- Perform a joint biopsy
- Treat with methotrexate
- Watch and wait
Differentials:

PA and lateral radiographs of left and right hands presenting with rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Classic signs:
- Symmetrical soft tissue swelling around affected joints that is fusiform
- Subluxations of damaged joints
- Marginal erosions, frequently on the radial side of metacarpophalangeal joints
- Joint space narrowing
- Spared DIPs
-------------------------------------
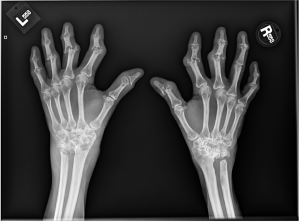
PA radiograph of left and right hands presenting with psoriatic arthritis
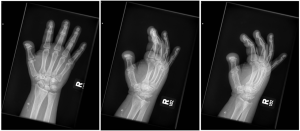
PA and oblique radiographs of right hand presenting with psoriatic arthritis
Psoriasis (Psoriatic arthritis)
Classic signs:
- Erosive change with bone proliferation in a predominantly distal distribution
- Classic “pencil-in-cup” deformity (but is not pathognomonic)
- Bone proliferation results in irregular, “fuzzy” appearance around the affected joint
- Joint space narrowing
-------------------------------------
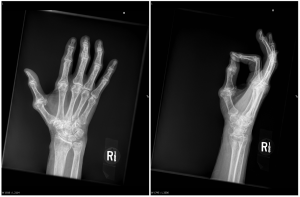
PA and lateral radiographs of right hand presenting with calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CPPD)
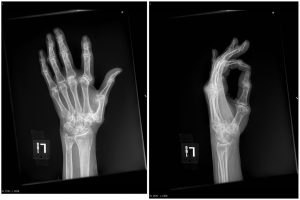
PA and lateral radiographs of left hand presenting with calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CPPD)
CPPD (Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease)
Classic signs:
- Tend to be symmetric in their distribution pattern and involve non-weight bearing joints
- Cartilage calcification seen as punctate and linear radiodensities in articular cartilage
-------------------------------------
Lateral and AP radiographs of left ankle presenting with gout
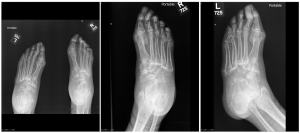
AP and oblique radiographs of left and right feet presenting gout
Gout
Classic signs:
- Lumpy and bumpy soft tissue swelling around affected joints
- Well-defined “punched-out” erosions with sclerotic margins (rat bite erosions) in a marginal and juxta-articular distribution
- Asymmetric distribution (most common at MTP joints
- Presence of tophi (monosodium urate crystal deposits) in surrounding soft tissues (this is pathognomonic)
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Shoulder dislocation
Aly Fawzy, Aleena Malik, Hayley McKee, Jacob Peller, Dr. Angela Atinga
Case Overview
Left anterior and inferior shoulder dislocation with no associated fracture.
Presentation
Mike is a 25 year-old-man presenting to the emergency department with a history of severe pain and tenderness in his left shoulder after sustaining a blow to his arm when playing basketball with friends 2 hours ago. He is able to pinpoint the pain near the distal left clavicle. Mike describes that his shoulder is swollen and discoloured (erythematous).
Physical Examination
Mike’s left arm is slightly abducted and externally rotated and he is resisting all movement. The acromion appears prominent and there is a loss of the normal rounded appearance of the left shoulder (“squared off” appearance). There is a loss of sensation on the lateral aspect of the left shoulder.
Imaging (3 X-Ray Views)
X-ray: Modified axial trauma view of the L shoulder. Humeral head is anterior to glenoid fossa.
X-ray: AP view of the L shoulder. Humeral head lies in the subcoracoid position, with anterior and inferior displacement from the glenoid fossa.
X-ray: Scapular “Y” view of the L shoulder. Anterior, inferior dislocation of humeral head from the glenoid fossa.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Review Questions
Question 1:
What if on physical examination Mike had difficulty abducting his arm and had a loss of sensation in a ‘shoulder patch’ distribution, what nerve is most commonly injured in the setting of a shoulder dislocation?
- axillary nerve
- musculocutaneous nerve
- radial nerve
- median nerve
- ulnar nerve
Answer: 1. axillary nerve
Explanation: The axillary nerve (C5-C6) is a branch of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. Due to its anatomical course around the surgical neck of the humerus, it is the nerve most commonly injured following shoulder dislocation. In a study of patients with anterior shoulder dislocations the axillary nerve was injured in 42% of patients (1). The axillary nerve innervates the deltoid, which is the strongest abductor of the shoulder joint. It also gives off a branch called the superior lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm which provides a sensory distribution often described as a ‘shoulder patch’.
Question 2:
Which of the following is not a characteristic radiographic finding of an anterior shoulder dislocation?
- humeral head is anterior to centre of “Mercedez-Benz” sign on transcapular view
- presence of Hills-Sachs lesion
- presence of bony Bankart lesion
- presence of reverse bony Bankart lesion
- sub-coracoid lie of the humeral head on AP view
Answer: 4. Presence of reverse bony Bankart lesion
Explanation: A bony Bankart lesion most commonly occurs in the setting of an anterior shoulder dislocation when there is an avulsion of the anterior glenoid rim. A reverse bony Bankart lesion occurs in the setting of a posterior shoulder dislocation in which there is avulsion of the posterior glenoid labrum. Thus a reverse bony Bankart lesion would not be expected in an anterior shoulder dislocation.
Question 3:
The Neer classification system is widely used to classify proximal humeral fractures. If Mike presented with a fracture line involving the greater and lesser tuberosities, as well as the anatomical neck of the humerus, without any displacement (i.e. <1 cm and <45°), what class of fracture would be reported?
- One-part fracture
- Two-part fracture
- Three-part fracture
- Four-part fracture
Answer: 1. One-part fracture
Explanation: The Neer classification system of proximal humeral fractures is based on four anatomical parts of the shoulder joint; the anatomical neck, the surgical neck, the greater tuberosity, and the lesser tuberosity (2). Neer classification assesses the presence or degree of displacement, which is defined as a segment being >1 cm from the normal anatomical position or >45° angulated. One-part fractures have no displacement, two-part have one displaced fragment, three-part have two displaced fragments but the humeral head remains in contact with the glenoid fossa, and four-part have three or more displaced fragments and dislocation of the humeral head from the glenoid fossa.
Question 4:
When would further imaging, such as a CT, be indicated in Mike’s case?
- For patients that are indicated for surgery or have recurrent instability
- In all patients 2 weeks after initial radiographs
- In all patients presenting with posterior shoulder dislocations
- In all patients above the age of 75
Answer: 1. For patients that are indicated for surgery or have recurrent instability
Explanation: In most cases, only radiographs are needed to accurately diagnose a shoulder dislocation. Specifically, the scapular “Y”, AP and axillary views are used to confirm shoulder dislocations. CT is rarely needed but can be indicated when closed reduction is insufficient and surgery is needed to repair the dislocation or other complications. CT has also been shown to be useful in assessing the amount of bone loss if there are Bankart and Hill-Sachs lesions present, as there have been studies that show a correlation between recurrent dislocations and increased bone loss from lesions (3).
Question 5:
Which of the following is the most common form of shoulder dislocations?
- Anterior dislocation
- Posterior dislocation
- Inferior dislocation
- Anterior and posterior dislocations are equally the most prevalent
Answer: 1. Anterior dislocation
Explanation: In the literature, it has been described that 95-97% of shoulder dislocations are anterior, 2-4% are posterior, and 0.5% are inferior dislocations (4).
References
- Visser CP, Coene LN, Brand R, Tavy DL. The incidence of nerve injury in anterior dislocation of the shoulder and its influence on functional recovery. A prospective clinical and EMG study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999 Jul;81(4):679-85. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.81b4.9005. PMID: 10463745.
- Sidor ML, Zuckerman JD, Lyon T, Koval K, Cuomo F, Schoenberg N. The Neer classification system for proximal humeral fractures. An assessment of interobserver reliability and intraobserver reproducibility. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 1993 Dec 1;75(12):1745-50.
- Shijith KP, Sood M, Sud AD, Ghai A. Is CT scan a predictor of instability in recurrent dislocation shoulder? Chin J Traumatol. 2019 Jun;22(3):177-181. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2019.01.010. Epub 2019 Apr 13. PMID: 31056471; PMCID: PMC6543279.
- Brady WJ, Knuth CJ, Pirrallo RG. Bilateral inferior glenohumeral dislocation: luxatio erecta, an unusual presentation of a rare disorder. J Emerg Med. 1995;13(1):37.
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Small Bowel Obstruction - Adenocarcinoma
Faran Chaudhry, Janet Tang, Chloe Campbell, Dr. Nasir Jaffer
Presentation
Crosby is a 64-year-old male presenting to his family physician for a 6-month history of progressive lethargy. He notes that he has also experienced unintentional weight loss and a vague, non-specific abdominal pain. Crosby describes the pain as “crampy” and intermittent. It does not radiate elsewhere. His pain is somewhat alleviated by an over-the-counter analgesic. There is no history of nausea, vomiting, or bleeding. He has a 25 pack-year smoking history and consumes 5-6 drinks of alcohol weekly. His diet largely consists of red meat. His past medical history is unremarkable. Other than the over-the-counter analgesic taken for abdominal pain, he does not regularly take any medications including NSAIDs, ASA, or glucocorticoids. However, his family history is significant for Crohn’s disease.
Physical Exam and Investigations
On physical examination Crosby presents with pallor. Otherwise, the physical examination is unremarkable. Initial investigations included a complete blood count (CBC), electrolytes, creatinine, liver function tests (LFT), carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), and carbohydrate antigen (CA 19-9). Significant findings include a low red blood cell count indicating anemia, likely stemming from occult bleeding. Both the CEA and CA 19-9 were also elevated.
What is the next best test for the management of this patient?
- Barium GI
- Upper and lower endoscopy
- Nuclear medicine scan
- CT with oral and IV portal phase
- Biphasic CT enterography (CTE)
Answer: 2
Explanation: Endoscopy can be expected to reveal a cause of occult GI bleeding in 30-50% of patients (located in the esophagus, stomach and or colon) with high sensitivity and specificity, and has the added advantage of concurrent biopsy. Barium Upper GI is a reasonable approach to diagnosis of esophago-gastric lesions and is non-invasive, but is less sensitive than endoscopy. Nuclear medicine scans used only when is a significant bleeding rate, and may be more useful to investigate Meckel’s Diverticulum in children. CT with oral and IV contrast/CTE is more beneficial assessing for small bowel lesions following normal upper and lower endoscopy (see the following question).
Case Continued
An upper endoscopy and colonoscopy were completed and revealed no abnormal findings.
What is the next best test for the management of this patient?
- Barium GI
- Nuclear medicine scan
- CT with oral and IV portal phase
- Biphasic CT enterography (CTE)
Answer: 4
Explanation: Once endoscopy is performed, and is negative, this may indicate a small-bowel source for obscure GI bleed. This best assessed with capsule endoscopy or CT imaging of the small bowel
Biphasic CT Enterography (CTE) is the next most reasonable approach.
- ORAL CONTRAST: It involves patient ingesting of neutral oral contrast media - Sorbitol. This provides optimal distention of the small bowel and maximal contrast between the lumen and small bowel wall to facilitate the detection of mucosa or mural abnormalities.
- INTRAVENOUS CONTRAST: CT is done as a Biphasic study – Arterial-Venous phases allows rapid diagnosis in the detection of a wide range of small bowel lesions as a cause of anemia. Some lesions such as angiodysplasia, carcinoid or neuroendocrine lesions, are best seen on the arterial phase of CT scan. Lesions such as adenocarcinoma, lymphoma can be seen on the venous phases of CT scans
Case Continued
What lesions in the small bowel present with occult anemia?
- Small bowel adenocarcinoma
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumour
- Celiac disease
- Meckel’s diverticulum
- Angiodysplasia
- Cancer metastasis
IMAGING
A CT scan with Oral and IV contrast (Venous Phase) was done.
What do you see?
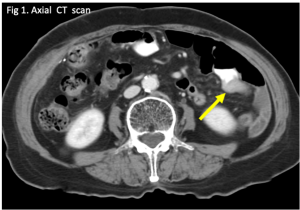
Figure 1: An axial CT scan of the abdomen with intravenous and barium oral contrast. There is a soft tissue lesion in the proximal jejunum (arrow), with no proximal small bowel dilatation.
What diagnosis would you consider?
- Small bowel adenocarcinoma
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumour
- Celiac disease
- Meckel’s diverticulum
- Angiodysplasia
- Cancer metastasis
ANSWER: There is a differential diagnosis for this solitary small bowel lesion
- Small bowel adenocarcinoma, lymphoma
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST)
- Cancer metastasis – from melanoma, lung cancer, breast cancer,
FINAL DIAGNOSIS (AFTER SURGERY)
The combined history, physical exam, investigations and surgery point towards an adenocarcinoma of the small bowel. A CT scan is completed to help support these findings.
Case 1: Adenocarcinoma of Proximal Jejunum Presenting as a Mass

Figure 1: An axial CT scan of the abdomen with intravenous and barium oral contrast. There is a soft tissue lesion in the proximal jejunum (arrow), with no proximal small bowel dilatation.
Diagnosis: Small bowel adenocarcinoma
Small bowel adenocarcinomas account for 25-40% of primary malignant small bowel tumours. They typically present in 50-70-year-old patients and arise from glandular epithelium. They most frequently occur in the proximal jejunum and distal duodenum. Common risk factors include Crohn’s disease and celiac disease. Patients usually present with vague symptoms including abdominal pain, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, and jaundice.
Potential Variations and Differential Diagnoses
Case 2: Adenocarcinoma of Proximal Jejunum Causing Low Grade Small Bowel Obstruction
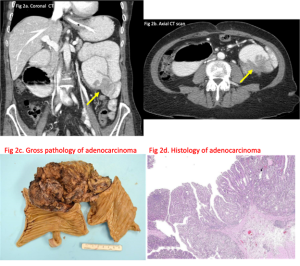
Figure 2: A coronal (a) and axial (b) CT scan with intravenous & barium oral contrast. There is an annular apple core constricting lesion in the proximal jejunum (arrows) with moderate proximal small bowel dilatation. Gross pathology (c) and histology of the lesion (d) suggesting adenocarcinoma.
Diagnosis: Small bowel adenocarcinoma
Case 3: Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumour (GIST) of Small Bowel
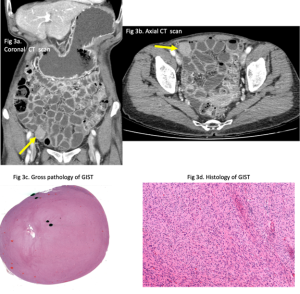
Figure 3: Coronal (a) and axial (b) CT scan with intravenous and neutral oral contrast (sorbitol). There is a 4 cm soft tissue lesion in distal ileum (arrows). Gross pathology (c) and histology of the lesion (d) suggesting GIST.
Diagnosis: Gastrointestinal stromal tumour of small bowel
Malignant gastrointestinal stroma tumours (GIST) are far less common than benign ones. These types of tumours are more common in male patients that are 65+. They are considered to be soft tissue sarcomas that arise from the interstitial cells of Cajal. GIST grow exophytically from the bowel wall and present quite late. These tumours also have areas of necrosis which can communicate with the small bowel lumen from which they originated. Node resections are generally not recommended in these tumours as they rarely metastasize.
Case 4: Celiac Disease
A 23-year-old female with 6-month history of watery diarrhea, crampy abdominal pain and weight loss is referred to a gastroenterologist. Blood tests for the patient are completed. An abdominal ultrasound was done in the radiology department as a screening test.
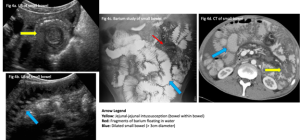
Figure 4: Ultrasound of small bowel revealing intussusception (a) and a fluid filled dilated small bowel (b). Barium study suggesting dilated small bowel with barium breaking up (fragments) in pool of water (c). CT of small bowel with intravenous and barium oral contrast depicting dilated small bowel and one segment showing jejunal-jejunal intussusception.
Diagnosis: Celiac disease
Celiac disease is a systemic autoimmune condition that is triggered by gluten in certain individuals that are genetically susceptible. It is most prevalent in European populations. Risk factors for celiac disease include having a first or second degree relative with celiac disease, type 1 diabetes mellitus, autoimmune thyroiditis, Down and Turner syndromes, and pulmonary hemosiderosis. Generally, it either presents asymptomatically or with microcytic (iron deficiency) anemia.
Case 5: Meckel’s Diverticulum
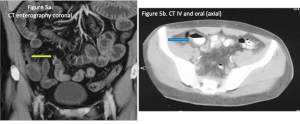
Figure 5: Coronal CT enterography (IV and oral sorbitol) showing (arrow) a small Meckel’s diverticulum (a). Axial CT (IV and barium oral contrast) showing (arrow) on another patient with a larger Meckel’s diverticulum (b).
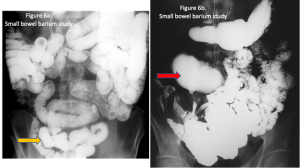
Figure 6: Small bowel barium study showing (arrow) a small Meckel’s diverticulum (a). Small bowel barium study on another patient showing (arrow) a large Meckel’s diverticulum (b).
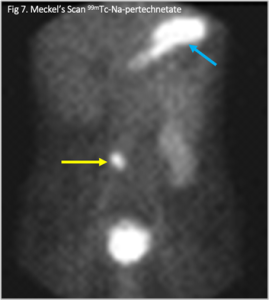
Figure 7: A Meckel’s scan depicting increased uptake of radiotracer in right lower quadrant by Meckel’s diverticulum containing gastric mucosa (yellow arrow). The stomach with gastric mucosa also takes up the radiotracer (blue arrow).
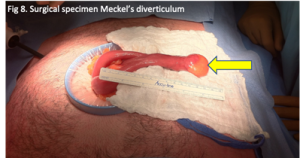
Figure 8: Surgical specimen of Meckel’s diverticulum (arrow).
Diagnosis: Meckel’s diverticulum
This is the most common genetic malformation of the gastrointestinal tract. It occurs in embryonic development with failure of regression of the omphalomesenteric duct, resulting in the formation of outpouchings in the small bowel wall that contain all intestinal layers from submucosa to adventitia, also known as true diverticula. Presentation follows the “rule of two”; Meckel’s diverticula occurs twice as commonly in males, with prevalence of 2% of the population, and occurs within the first two years of life. Diverticula are also typically about 2 inches long, within 2 feet of the ileocecal valve, and cause two predominant symptoms (bleeding and obstruction). It can also present with ulcerations, intestinal obstruction, hemorrhage, intussusception, and perforation. Meckel’s diverticulum is especially common in the pediatric population, although it is often undiagnosed in adult patients. Complications include diverticulitis, bleeding, bowel obstruction, enterolith formation, perforation, and neoplasm.
Case 6: Angiodysplasia
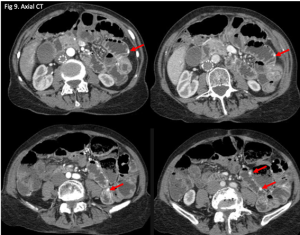
Figure 9: Arterial phase CT scan showing multiple small vascular malformations (arrows).
Diagnosis: Angiodysplasia
Angiodysplasias are defined as abnormal/tortuous vessels lacking smooth muscle, and are the most common vascular abnormality of the GI tract. Etiology is unclear, and it is not known to be related to any hereditary or systemic conditions. Angiodysplasia can be diagnosed readily with CT or angiography, although diagnosis may be difficult as many patients are asymptomatic. They often present in older patients as a frequent cause of lower GI bleeding. It presents clinically across a broad spectrum - from an incidental finding, to occult bleeding, and to an acute massive hemorrhage. Treatment options vary greatly, depending on the severity of the abnormality and presentation.
Case 7: Metastasis from Sarcoma of Left Leg
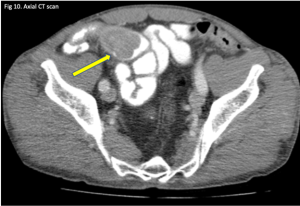
Figure 10: CT scan of small bowel showing a lobulated intraluminal mass in distal ileum (arrow). Pathology at surgery indicated a metastasis from sarcoma of left leg.
Diagnosis: Sarcoma metastasis
Metastatic lesions to the small bowel from various cancers (such as breast cancer, melanoma, lung cancer, etc.) are more common than primary malignancy to the small bowel. Sarcomas specifically represent 10% of all small bowel cancers. The most common sarcoma in the small bowel are leiomyosarcomas. Although sarcoma metastases are quite rare, they often present late, and therefore yield a very poor prognosis despite being slow growing. They primarily arise from muscle tissue and most often presents in the jejunum, then the ileum and duodenum. Patient presentation commonly includes bleeding, as well as perforation. Treatment includes resection and radiation therapy.
Other metastatic lesions to small bowel include melanoma, breast and lung cancer and rarely osteosarcoma
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Questions
Question 1. What is the most common GI source of anemia?
- Adenocarcinoma
- Crohn’s disease
- Angiodysplasia
- Celiac disease
Answer: 3
Question 2. What is the best way to confirm the diagnosis of Celiac disease?
- Positive celiac serology (tTG antibody + IgA level) and CTA
- Typical duodenal histological changes (villous atrophy + crypt hyperplasia) and CTA
- History and typical duodenal histological changes (villous atrophy + crypt hyperplasia)
- Positive celiac serology (tTG antibody + IgA level) and typical duodenal histological changes (villous atrophy + crypt hyperplasia)
Answer: 4
Question 3. If the patient in the case reports additional symptoms of nausea/vomiting, early satiety, and constipation, which of the following endoscopic procedures should be avoided?
- Colonoscopy
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
- Push enteroscopy
- Capsule endoscopy
Answer: 4
Explanation: The aforementioned symptoms are manifestations of small bowel obstruction. Capsule endoscopy involves swallowing a small pill-shaped capsule equipped with a wireless camera that takes pictures as it passes through the GI tract. It should not be performed in patients with suspected small bowel obstruction since the capsule may become lodged and require laparotomy for retrieval. A colonoscopy can access up to most of the terminal ileum and is appropriate for examining the distal small bowel for obstructive masses. An EGD can reach down to the second part of the duodenum and is appropriate for examining the proximal small bowel for obstructive masses. If neither colonoscopy nor EGD reveal positive findings, push enteroscopy may be considered to gain access beyond the Ligament of Treitz.
Question 4. What is the best initial investigation when small bowel bleeding is suspected, according to American College Guidelines?
- Endoscopy and/or small bowel evaluation
- Video capsule endoscopy
- CTE/MRE
- Meckel’s scan
Answer: 1
Question 5. In which cases may radionuclide imaging be beneficial?
- Following angiography for GI bleed
- Elderly patients who are suspected to have a small bowel bleed
- Patients with small bowel blood loss of at least 0.1-0.5 mL/min
- Patients with acute lower GI bleeding
Answer: 3
References
Aparicio, T., Zaanan, A., Svrcek, M., Laurent-Puig, P., Carrere, N., Manfredi, S., Locher, C., & Afchain, P. (2014). Small bowel adenocarcinoma: Epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. Digestive and Liver Disease, 46(2), 97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2013.04.013
Barth,iK.H. (1995). Radiological intervention in upper and lower gastrointestinal oooobleeding.BaillieresClinGastroenterol,19(1),53-69.doi:10.1016/0950-3528(95)90070-5
Ciresi, D. L., & Scholten, D. J. (1995). The continuing clinical dilemma of primary tumors of the small intestine. The American Surgeon, 61(8), 698–702; discussion 702-703.
Dahlerup, J. F., Eivindson, M., Jacobsen, B. A., Jensen, N. M., Jørgensen, S. P., Laursen, S. B., Rasmussen, M., & Nathan, T. (2015). Diagnosis and treatment of unexplained anemia with iron deficiency without overt bleeding. Danish Medical Journal, 62(4), C5072.
Fasano, A., & Catassi, C. (2012). Celiac Disease. New England Journal of Medicine, 367(25), 2419–2426. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp1113994
Goddard, A. F., McIntyre, A. S., & Scott, B. B. (2000). Guidelines for the management of iron deficiency anaemia. British Society of Gastroenterology. Gut, 46 Suppl 3-4, IV1–IV5. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.46.suppl_4.iv1
Goldberg, S. L., Fink, V., & Goldsmith, B. (1963). Metastatic Osteogenic Sarcoma of the Ileum: Intussusception and Intestinal Obstruction. Archives of Surgery, 86(2), 233–234. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1963.01310080057013
Huprich, J. E., Barlow, J. M., Hansel, S. L., Alexander, J. A., & Fidler, J. L. (2013). Multiphase CT enterography evaluation of small-bowel vascular lesions. AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology, 201(1), 65–72. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.12.10414
Ilangovan, R., Burling, D., George, A., Gupta, A., Marshall, M., & Taylor, S. A. (2012). CT enterography: Review of technique and practical tips. The British Journal of Radiology, 85(1015), 876–886. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/27973476
Incidence, treatment and outcome of abdominal metastases in extremity soft tissue sarcoma: Results from a multi‐centre study—PMC. (n.d.). Retrieved August 22, 2022, from https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.myaccess.library.utoronto.ca/pmc/articles/PMC7065201/
Jasti, R., & Carucci, L. R. (2020). Small Bowel Neoplasms: A Pictorial Review. RadioGraphics, 40(4), 1020–1038. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2020200011
Legué, L. M., Bernards, N., Gerritse, S. L., van Oudheusden, T. R., de Hingh, I. H. J. T., Creemers, G.-J. M., ten Tije, A. J., & Lemmens, V. E. P. P. (2016). Trends in incidence, treatment and survival of small bowel adenocarcinomas between 1999 and 2013: A population-based study in The Netherlands. Acta Oncologica, 55(9–10), 1183–1189. https://doi.org/10.1080/0284186X.2016.1182211
Mullangi, S., & Lekkala, M. R. (2021). Adenocarcinoma. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562137/
Ohmiya, N. (2020). Management of obscure gastrointestinal bleeding: Comparison of guidelines between Japan and other countries. Digestive Endoscopy, 32(2), 204–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/den.13554
Quinones, G. A. O., Suheb, M. Z. K., & Woolf, A. (2022). Small Bowel Cancer. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560725/
Raghav, K., & Overman, M. J. (2013). Small bowel adenocarcinomas—Existing evidence and evolving paradigms. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 10(9), 534–544. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.132
Richter, J. M., Christensen, M. R., Colditz, G. A., & Nishioka, N. S. (1989). Angiodysplasia: Natural history and efficacy of therapeutic interventions. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 34(10), 1542–1546. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01537107
Sagar, J., Kumar, V., & Shah, D. K. (2006). Meckel’s Diverticulum: A Systematic Review. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 99(10), 501–505. https://doi.org/10.1177/014107680609901011
The elusive small bowel adenocarcinoma in the terminal ileum—A case report—PMC. (n.d.). Retrieved August 22, 2022, from https://www-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.myaccess.library.utoronto.ca/pmc/articles/PMC5994869/
Wells, M. L., Hansel, S. L., Bruining, D. H., Fletcher, J. G., Froemming, A. T., Barlow, J. M., & Fidler, J. L. (2018). CT for Evaluation of Acute Gastrointestinal Bleeding. RadioGraphics, 38(4), 1089–1107. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2018170138
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Spinal Trauma
Tiffany Ni*, Tania Saha*, Shayan Yazdan-Ashoori*, Kieran Murphy
*all authors contributed equally to this work
Case: spinal metastasis from primary lung malignancy
Introduction
Medical imaging plays a critical role in diagnosing and managing spinal cord compression. The rapid and appropriate selection of imaging modalities for patients with spinal cord pathologies can greatly reduce the risk of downstream neurological morbidity and mortality.
Comprised of 33 vertebrae (7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 4 coccygeal), the spinal column provides the body’s structural support and protects the spinal cord and exiting nerve roots1. A wide variety of etiologies can cause spinal cord compression, from traumatic motor vehicle accidents, falls, and sports-related injuries to primary spinal cord malignancy, spinal epidural abscess, to metastatic disease of the spine1.
Of the patients with an active malignancy, 2.5 to 5% of individuals may develop metastatic spinal cord compression (MSCC), which can spread from the primary site through several routes, including venous hematogenous spread versus arterial spread, direct tumor extension, or lymphatic spread2. A previous investigation found that lung cancer, prostate cancer, and multiple myeloma comprised most hospitalizations related to MSCC3. The most commonly implicated spinal level was the thoracic vertebrae, followed by the lumbar and cervical vertebral levels4. MSCC is typically caused by the collapse or compression of a vertebral body containing metastatic disease but can also be caused by direct tumor extension into the vertebral column1.
We report the case of a patient with new onset thoracic spinal cord compression from an extension of primary lung malignancy.
Patient presentation
A 59-year-old male presented to the emergency department (ED) with severe bilateral upper back stiffness and pain (numerically rated a “10”) and progressively worsening bilateral weakness of his lower limbs. His medical history includes lung cancer and hypertension. He has a 35 pack-year smoking history. His hypertension is managed with ramipril.
The patient’s back stiffness and pain was persistent but tolerable for two months. However, the day prior to presenting to the ED, the pain substantially increased. Over the course of the day, his back pain worsened, and he was unable to engage in his daily activities. His pain increased in severity with sneezing and passing stool. The next morning, he had difficulty getting out of bed and walking due to newly developed paraparesis, in addition to newly developed urinary hesitancy and one bowel movement accident. By the time he arrived at the hospital, he had also lost sensation in his lower limbs and was barely able to walk.
Physical Exam
The patient had a blood pressure of 135/85 mmHg, heart rate of 90 bpm, respiratory rate of 17 breaths/minute, and an oral temperature of 37oC. His oxygen saturation level in room air was 97%. His back pain was exacerbated with palpation and percussion of the spine, as well as with the Valsalva maneuver. On neurologic examination, he had significant lower limb weakness (1/5) and absent sensation and proprioception. His lower limb reflexes were absent in both lower limbs, but normal in his upper limbs (2+). Anal sphincter tone was reduced on digital rectal examination. The patient also had decreased sensation in areas surrounding and adjacent to his anus, including the perineum and buttocks (saddle anesthesia).
Differential diagnosis
- Cord compression
- Spinal cord infarct
- Compression fracture
- Spinal stenosis
- Spinal epidural abscess
- Spinal subdural hematoma
- Peripheral nerve sheath tumor
- Spinal meningioma
- Neurofibroma
- Schwannoma
Imaging
To make the diagnosis of spinal cord compression, an urgent MRI of the spine should be performed.
Radiographic features:
CT
- Non-contrast: hyperdense extradural mass
MRI
- T1: isointense or hyperintense to spinal cord
- T2: heterogeneously hyperintense to spinal cord with hypointense foci
Figure 1: T1 Sagittal MRI
A pre-vertebral and post-vertebral lesions of the T2-T3 spinal cord (as outlined in blue).
Figure 2: T2 Sagittal MRI
A pre-vertebral and post-vertebral lesions of the T2-T3 spinal cord (as outlined in blue).
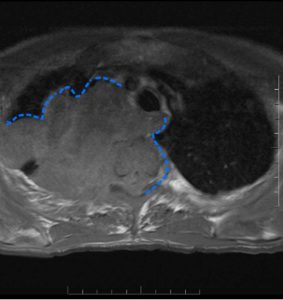
Figure 3: T1 Axial Non-Contrast MRI
Metastatic lesion compression of the mediastinum and the spinal cord (as outlined in blue).
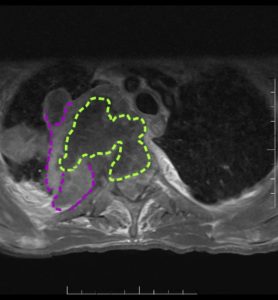
Figure 4: T1 Axial MRI + Gadolinium
Metastatic lesion with compression of the spinal cord with hypodense center, and hyperdense borders (as outlined in purple). Hypodense indicating tumor ischemia (as outlined in green).
Conclusion
An urgent MRI was required to make the proper diagnosis. The patient was diagnosed with metastatic lung cancer in which the tumor has grown directly from the lung into the vertebrae and spinal canal. As the patient was not surgical candidate, they were placed in palliative care.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Questions
Question1. In a person with suspected lung cancer, what would be the most appropriate initial imaging selection?
- X-ray
- CT Scan
- MRI
Answer: 2
A CT scan is the most appropriate when someone is suspected of lung cancer then further investigations can be done with MRI to identify the size and spread.
Question 2. What radiographic features would you expect to see with an MRI T1 scan with contrast of a metastatic spinal cord compression?
- Hypodense and hyperdense lesion
- Non-enhancing margins
- Homoegenous enhancement of tumor
- Enhancement of necrotic core
Answer: 1
A T1 scan with contrast would allow to better visualization of peripheral and nodular enhancement of the tumor through hypodense and hyperdense regions that indicate necrotic or growing tissue.
Question 3. What feature(s) on imaging would make you most suspicious for metastatic spinal cord compression?
- Metastatic deposits in a vertebral body spreading into the epidural space
- Metastatic deposits in a vertebral body spreading to the spinous process
- Primary lung tumor
- Metastatic deposits along the sternum with accumulation of blood in the epidural space
Answer: 1
When vertebral metastases spread into the epidural space, there can be direct compression of the spinal cord. The specific features that may be visible on MRI include narrowing of the spinal canal and displacement of the spinal cord.
(4) is a spinal epidural hematoma, which can compress the spinal cord and cause similar neurological deficits as seen in this case but is not the correct answer because it is not the metastatic mass itself causing the spinal cord compression and the history is very different.
Question 4. In a patient yet to be treated for spinal cord compression with loss of lower limb motion, such as in this case, what are the most important prognostic factors for regaining lower limb function?
- Speed with which neurologic symptoms developed
- Severity of pain and whether it initiated suddenly vs. gradually
- Neurologic status and duration of lower limb symptoms/ambulatory loss
- Ability to move the upper limbs and other areas of the body
- Whether the spinal cord compression was secondary to metastasis or another cause such as trauma
Answer: 3
While all of the options are important to consider in a patient with spinal cord compression, when seeing a patient with ambulatory loss, their pre-treatment neurologic status and duration of ambulatory loss are the most important prognostic factors in determining their likelihood to regain ambulation once treated. For instance, a patient who has been non-ambulatory for over two days before presenting to the doctor is less likely to regain their ability to walk than someone who was non-ambulatory for under one day. In the same sense, severe paraparesis has a worse prognosis than milder paraparesis. For this reason, early detection and diagnosis of spinal cord compression is of utmost importance.
https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.myaccess.library.utoronto.ca/27488300/
Question 5. Which of the following treatment options is the best of the management of metastatic spinal cord compression?
- Corticosteroids
- Radiotherapy
- Percutaneous procedures (e.g., bone biopsy to get tissue for diagnosis.)
- Surgery
- All of the above
Answer: 5
The treatment for metastatic disease of the spine is multifaceted and may depend on the presentation of the disease, severity of the symptoms, and the prognosis of the patient.
Question 6. Following MRI confirmation of metastatic spinal cord compression, what does the initial management of this condition consist of?
- Intravenous bisphosphonate
- Analgesia and consultation with oncology team
- Dexamethasone only
- Dexamethasone with proton pump inhibitor
- Vertebroplasty for the affected spinal levels
Answer: 4
Dexamethasone (iv and then oral) with proton pump inhibitor should be prescribed initially. High-dose dexamethasone is associated with severe gastrointestinal toxicity, including bowel perforation, ulceration, and bleeding. Proton pump inhibitor is prescribed in combination as prophylaxis against dexamethasone-induced ulceration.
References
- Robson, P. Metastatic spinal cord compression: a rare but important complication of cancer. Clin. Med. 14, 542–545 (2014).
- Dunning, E. C., Butler, J. S. & Morris, S. Complications in the management of metastatic spinal disease. World J. Orthop. 3, 114–121 (2012).
- Mak, K. S. et al. Incidence and treatment patterns in hospitalizations for malignant spinal cord compression in the United States, 1998-2006. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 80, 824–831 (2011).
- Yu, H.-H. M., Maranzano, E. & Rades, D. Chapter 12 - Palliative Radiotherapy for Malignant Epidural Spinal Cord Compression. in Handbook of Supportive and Palliative Radiation Oncology (eds. Krishnan, M. S., Racsa, M. & Yu, H.-H. M.) 169–188 (Academic Press, 2017). doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-803523-8.00012-5.
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Young Patient with Rectal Bleeding – Ulcerative Colitis
Muhammad Uzair Khalid, Samantha Macpherson, Lara Parlatan, Dr. Nasir Jaffer
Clinical History
Craig Walters (CW) is a 26-year-old male who presents to his family physician with a seven-week history of loose stool and intermittent cramping with abdominal pains. CW is visibly concerned, emphasizing that the frequency of his bowel movements have increased from two times per day to now averaging six times daily. He also reports increased urgency and some episodes of bright red blood in his stool. Craig states that he has been having trouble during his shifts at work because he feels more tired and tenesmus is interfering with his concentration. Craig has tried omitting gluten and dairy from his diet but this has not helped to alleviate his symptoms. He does not have a history of smoking. He only drinks socially. He is not on any medications except an over-the-counter multivitamin.
Physical Exam and Investigations
Upon general inspection Craig appears well with no acute signs of distress. Craigs heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure are in the normal range and he has a temperature of 37°C. Craig currently denies having any abdominal pain during his visit. There are no remarkable findings from an abdominal examination, including a perianal exam, precordial assessment or respiratory assessment. Initial investigations included a complete blood count CBC, electrolytes, creatine, C-reactive protein (CRP), and stool culture. Significant findings included low Hb-count and low iron, increased CRP, WBC and platelet count.
Given the information presented so far, what do you think is the most likely diagnosis? Consider the patient’s age.
- Ulcerative colitis
- Hemorrhoids
- Anal fissure
- Rectal carcinoma
ANSWER: 1
The patient is a young (26-year-old) male. Combined with the history of chronic loose stools, abdominal pains, and increasing frequency and urgency of CW’s bowel movements, CW’s age makes ulcerative colitis the most likely diagnosis. Hemorrhoids are unlikely given both the patient’s age, as well as the clinical history of diarrhea and normal perianal physical exam. He has had no pain with defecation, ruling out an anal fissure. Rectal carcinoma is unlikely given that the patient is young and there are no category B symptoms (fever, weight loss, night sweats, chills).
What is the next best investigation?
- CT Abdomen
- Abdominal x-ray
- MRI
- Colonoscopy
- Barium Enema
- CT Colonography
ANSWER: 4
Colonoscopy is the gold-standard to diagnose ulcerative colitis. Markers of chronic inflammation on colonoscopy include erythema, edema, erosions, and petechiae.
On biopsies, findings would include crypt abscesses, shortening, branching and atrophy; epithelial cell mucin depletion; and increased lamina propria cellularity. Two or more histologic features on endoscopy support a diagnosis for ulcerative colitis.
Figure 1. Colonoscopy images of severe acute ulcerative colitis. Loss of normal vascular pattern is shown, as well as deep and superficial ulcers (blue and yellow arrows respectively).
CT Abdomen has no role to play in the initial diagnosis of ulcerative colitis, and only comes into play when investigating acute flares and chronic complications.
Abdominal Radiographs are only used when assessing for complications in acute flare i.e., megacolon or bowel perforation.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the colon is too limited and costly to be a first-line diagnostic tool for ulcerative colitis and not used either for acute flare or to assess complications.
Barium enema is no longer used to assess any type of colonic diseases including polyps, IBD or colonic symptoms (see Figure 2).
CT Colonography is a technique where patient undergoes bowel cleansing and insufflation of colon with CO2 to detect colonic polyps. Prone and supine low-dose CT scans are done with no IV contrast (see Figure 3).
Figure 2. Double contrast Barium enema. Fine granularity of mucosa (arrow) is shown. The patient’s colonoscopy view shows severe ulcerations. Barium enemas are no longer used.
CT COLONOGRAPHY: Technique for screening colonic polyps
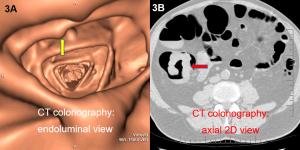
Figure 3. CT colonography. An endoluminal view (3A) of CT colonography shows multiple polyps (yellow arrow) with a diagnosis of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP). An axial CT image (3B) from CT colonography shows large apple core cecal cancer (red arrow).
Medical management
CW underwent a colonoscopy, showing extensive left-sided colitis (see Figure 1). Subsequently, CW was initially treated with a combination of oral 5-ASA/sulfasalazine (also known as mesalamine) at 4g once daily and rectal mesalamine enemas once daily. Symptomatic improvement was seen within three weeks. Patient became asymptomatic after six weeks of therapy, and was instructed to stay on oral mesalamine at 3g daily, with discontinuation of the rectal enemas. However, the patient was lost to follow-up.
Case continued – 2 years later…
CW presented to the emergency department 2 years later with increasing bouts of bloody diarrhea (7 times per day), high fever at 38.1°C, HR 121 bpm, and marked abdominal distention. The patient also admits to poor adherence to his medications, as he felt that these were no longer necessary. Labs showed elevated WBC count, decreased Hb, and hypokalemia. Given the patient’s severe presentation, CW is admitted for monitoring and further investigation.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- toxic megacolon
- bowel obstruction
- gastroenteritis
- anal fissures
Answer: 1
Given the patient’s severe presentation, history of ulcerative colitis, and poor follow-up, a toxic megacolon is most likely. Whereas D can be ruled out on history, B and C cannot be effectively ruled out.
What is the next best study for the patient’s most likely diagnosis?
- Plain X-Ray
- MRI
- Low Dose Abdominal Tomogram (CT tomogram)
- Colonoscopy
ANSWER: 1 or 3
A plain abdominal x-ray is most appropriate for investigating toxic megacolon. At some centers, however, an ultra-low dose CT is used to assess the extent of ulcerative colitis for megacolon and possible perforation that may lead to an urgent surgery. A colonoscopy is not indicated in an acute flare, as it may cause a perforation in the colon. An MRI is also not indicated, given the more accessible options.
To investigate CW’s new and worsening symptoms an abdominal x-ray was performed (Figure 4).
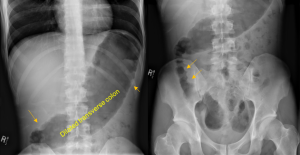
Figure 4. Supine abdominal x-ray. Colitis is seen, including thumbprinting of the ascending colon haustra (orange arrows) with megacolon (dilated transverse colon >6cm).
Diagnosis: Toxic Megacolon
Megacolon is a serious complication of inflammation in ulcerative colitis. This is diagnosed through a combination of clinical features and X-rays. In imaging, colitis can be identified, and the caliber of the colon should be noted as greater than 6 cm. In a patient with toxic megacolon, the deeper smooth muscle layer of the colon is inflamed.
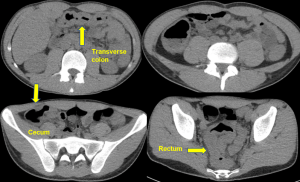
Figure 5. Low-dose abdominal tomogram for acute flare of UC. Thickened colon from rectum to cecum is shown (arrows).
Resolution
Medical management
After the diagnosis of toxic megacolon 5-ASA treatment must be put on hold as it can precipitate disease severity. CW is started on IV hydrocortisone by continuous infusion, and is responsive to initial therapy. If the megacolon is toxic and non-responsive to treatment that is an indication to perform surgery.
10 years later…
CW is now attending regular follow-ups for his UC. As per Canadian guidelines, he has continued to receive a routine colonoscopy starting 8 years after first onset of symptoms, once every 3 years. At his third colonoscopy, however, the patient is found to have colonic stricture on his routine colonoscopy. Patient had CT enterocolonography done (see Figure 6) for staging of the tumor. Following this finding, he needs further follow-up to rule out cancer. He is also referred to an oncologist.
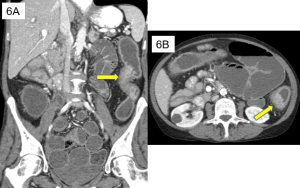
Figure 6. CT findings show a 5cm stricture in the descending colon (arrow) in coronal (6A) and axial (6B) views, suggesting an adenocarcinoma. CT is performed with IV contrast, and the technique includes a mild laxative followed by oral sorbitol and rectal water.
Further Imaging Studies and Findings in Acute Flare
1. Acute Flare Complications: Megacolon and Bowel Perforation
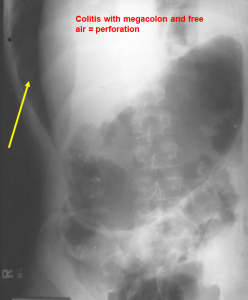
Figure 7A. Left lateral decubitus abdominal radiograph. Megacolon is seen, as well as thumbprinting and free intraperitoneal air (yellow arrow), suggesting bowel perforation most likely from the cecum.
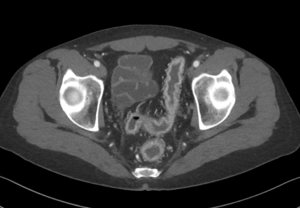
Figure 7B. CT scan with IV contrast. The rectum shows intense mucosal enhancement and increased mesenteric vascularity indicative of acute UC.
2. Imaging Studies and Findings in Chronic Ulcerative Colitis
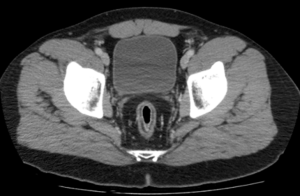
Figure 8. CT scan of pelvis with IV contrast. Chronic UC dark layer in inflamed tissue indicates fibrosis, which occurs with chronic UC.
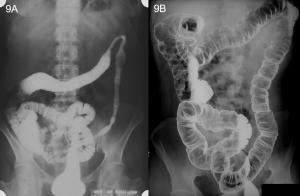 Figure 9. Single contrast barium enema. A featureless colon (9A) is seen with loss of haustra and narrowing of left colon. This is compared with a normal double contrast barium enema (9B).
Figure 9. Single contrast barium enema. A featureless colon (9A) is seen with loss of haustra and narrowing of left colon. This is compared with a normal double contrast barium enema (9B).
3. Imaging for Potential Variations and Differential Diagnoses including C. difficile colitis, hemorrhoids, polyposis syndrome, and acute/chronic U/C.
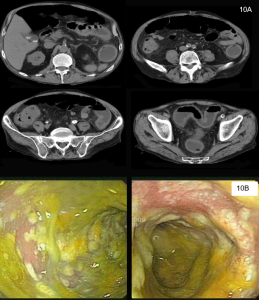
Figure 10. Infectious colitis. CT scan (10A) shows thickening of colon from cecum to rectum. Colonoscopy (10B) will show inflamed bowel with friable yellowish membranes. Whereas the imaging findings are similar to UC, the clinical history is usually different with non-bloody diarrhoea and fever.
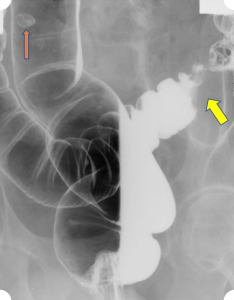
Figure 11. Sigmoid adenoma and sigmoid carcinoma. A double contrast barium enema shows a small polyp (adenoma) in the sigmoid colon (orange arrow) and an apple core lesion (carcinoma) in the sigmoid colon (yellow arrow).
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Review Questions
Question 1. What is the most common age for onset of ulcerative colitis?
-
- <30 years
- 30-50 years
- 50-65 years
- >65 years
ANSWER: 1 (<30 years).
Question 2. Which of the following is usually a last-stage complication of ulcerative colitis?
-
- Loose stools
- Toxic megacolon
- Bowel perforation
- Cancer
ANSWER: 4 (Cancer).
Question 3. What sign on abdominal x-ray is most indicative of ulcerative colitis being confined to the rectum (i.e., ulcerative proctitis)?
-
- Double duct sign
- Stool sign
- Hyperdense crescent sign
- Peritoneal stripe sign
ANSWER: 2 (Stool sign)
Question 4. Which of the following is used to investigate acute flares of ulcerative colitis?
-
- Ultra low dose non-contrast CT
- Ultrasound
- Colonoscopy
- Abdominal x-ray
ANSWER: 1 (Ultra low dose non-contrast CT) or D (abdominal x-ray)
References
A-Rahim Y.I., Farrell R.J. (2022). Overview of azathioprine and mercaptopurine use in inflammatory bowel disease. Up To Date. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-azathioprine-and-mercaptopurine-use-in-inflammatory-bowel-disease
Cohen R.D. Stein A.C. (2022) Management of moderate to severe ulcerative colitis in adults. Up To Date. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/management-of-moderate-to-severe-ulcerative-colitis-in-adults
Hashash J.A. and Regueiro M. (2022). Medical management of low-risk adult patients with mild to moderate ulcerative colitis. Up To Date. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/medical-management-of-low-risk-adult-patients-with-mild-to-moderate-ulcerative-colitis.
Hohmann E.L., Ananthakrishnan A.N., Deshpande V. (2014). Case 25-2014 — A 37-Year-Old Man with Ulcerative Colitis and Bloody Diarrhea. N Engl J Med; 371: 668-675.
Kaenkumchorn T., Wahbeh G. (2020). Ulcerative Colitis: Making the Diagnosis. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 49(4); 655-699.
Lee L., Saltzman J.R. (2021). Overview of colonoscopy in adults. Up To Date. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-colonoscopy-in-adults.
Peppercorn M.A., Kane S.V. (2022). Clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and prognosis of ulcerative colitis in adults. Up To Date. Available from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-and-prognosis-of-ulcerative-colitis-in-adults#:~:text=Colitis%20%E2%80%94%20Patients%20with%20ulcerative%20colitis,%2C%20and%20incontinence%20%5B1%5D.
Mark J. Roggeveen M.J., Tismenetsky M., Shapiro R. (2006). Best Cases from the AFIP: Ulcerative Colitis. RadioGraphics; 26(3): 947-951.
Do you have feedback for us? Fill out this form to share your thoughts!
Emergency Trauma: A Radiology Practice Case
Matthew C. Mueller, Dr. Ferco H. Berger
Presentation
Louis is a 28-year-old male coming via ambulance to the emergency department trauma bay after falling from 2-stories of scaffolding at a construction job site. He landed on his left side on the flat roof of a steel construction vehicle. He was wearing a hardhat, steel-toe boots and denies any head trauma
On past medical history, he has no prior diagnoses, no previous surgical history, and he has no prescription medications or allergies.
Physical Exam
His vitals are as follows: HR 130; RR 36; BP 90/77 mmHg; O2 saturation 87% on room air.
On exam, he appears in severe respiratory distress but is alert and oriented with a GCS of 14. His respiratory exam is notable for absent breath sounds in the left lung. He has severe abdominal pain, especially in the left upper quadrant.
Imaging and Investigations
A FAST exam is performed, which he tolerates poorly in the LUQ.
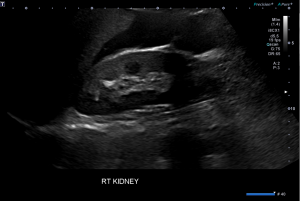
Figure 1: US of RUQ showing interface between kidney and liver
Question 1: What is the notable finding in this view of Morrison's pouch in the RUQ?
Answer: FAST exam reveals hypoechoic free-fluid in Morrison's pouch (interspersed between kidney and liver), which is indicative of hemoperitoneum as a result of the trauma.
A STAT portable AP Chest radiograph is performed.
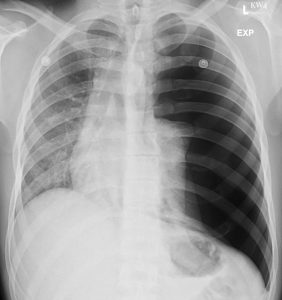
Figure 2: Chest radiograph
Question 2: Which radiological finding explains the severe shortness of breath?
Answer: Chest radiograph reveals a complete collapse of the left lung with displacement of the cardiomediastinal structures to the right, in keeping with a tension pneumothorax.
A left-sided wide bore chest tube is placed and the patient is sent for STAT CT of his chest and abdomen/pelvis.
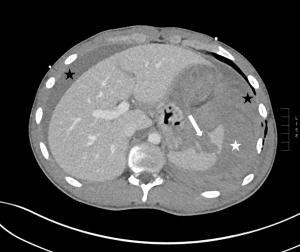
Figure 3: CT Abdomen
Question 3: What are the notable findings in the CT?
Answer: Splenic laceration (white arrow) with large subcapsular hematoma (white asterisk) with hemoperitoneum bordering the spleen and liver (black asterisks). There is no pseudoaneurysm, nor active contrast extravasation.
American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) splenic injury scale
- grade I
- subcapsular hematoma <10% of surface area
- parenchymal laceration <1 cm depth
- capsular tear
- grade II
- subcapsular hematoma 10-50% of surface area
- intraparenchymal hematoma <5 cm
- parenchymal laceration 1-3 cm depth
- grade III
- subcapsular hematoma >50% of surface area
- intraparenchymal hematoma ≥5 cm
- parenchymal laceration >3 cm depth
- ruptured subcapsular or intraparenchymal hematoma
- grade IV
- any injury in the presence of a splenic vascular injury* or active bleeding confined within splenic capsule
- parenchymal laceration involving segmental or hilar vessels producing >25% devascularization
- grade V
- shattered spleen
- any injury in the presence of splenic vascular injury* with active bleeding extending beyond the spleen into the peritoneum
Question 4: Based on the image provided, what grade would you consider this splenic injury to be?
Answer: AAST grade III
Based on the severity of the injury and the patient's hemodynamic instability, the patient was treated with an open splenectomy, at which point the hemorrhage was definitively controlled and the patient's vitals stabilized.
References
Kozar R, Crandall M, Shanmuganathan K et al. Organ Injury Scaling 2018 Update: Spleen, Liver, and Kidney. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2018;85(6):1119-22. doi:10.1097/ta.0000000000002058
Napoli A, Catalano C, Silecchia G et al. Laparoscopic Splenectomy: Multi–Detector Row CT for Preoperative Evaluation. Radiology. 2004;232(2):361-7. doi:10.1148/radiol.2322030445
www.aast.org. Injury Scoring Scale.
Full-Colour Atlas
Microcalcifications
The left mammogram depicts microcalcifications, as can be seen with DCIS.
The right mammogram depicts microcalcifications after surgical excision with needle localization.
Mammography
Normal Mammography
The left image is of a normal craniocaudal view of a breast mammogram.
The right image is that of a normal mediolateral oblique view of a breast mammogram.
Rotation
To assess rotation of the film, compare the distance between a spinous process to each of the clavicles. If the supinous process is closer to one clavicle, that side is rotated posteriorly.
Degree of Inspiration
To ensure proper inflation, the 6th rib should be visible anteriorly and the 10th rib posteriorly.
Ureteric Obstruction
Observe the obstructive lesion near the lower end of the right ureter. On simultaneous retrograde examination, the lower margin of the obstructing lesion is clearly demarcated.
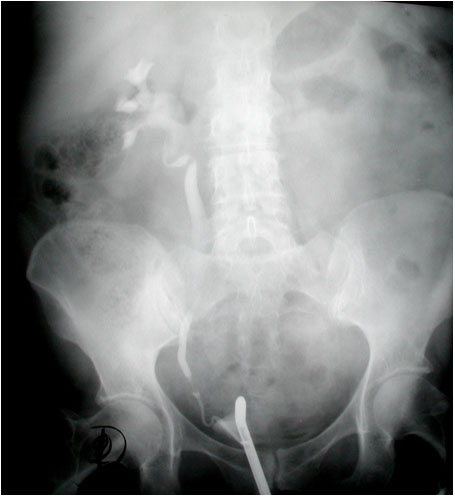
Intravenous pyelogram
Intravenous pyelogram (IVP) (1 hour post-dye injection) showing right hydronephrosis, hydroureter, dilated renal pelvis and calvx.
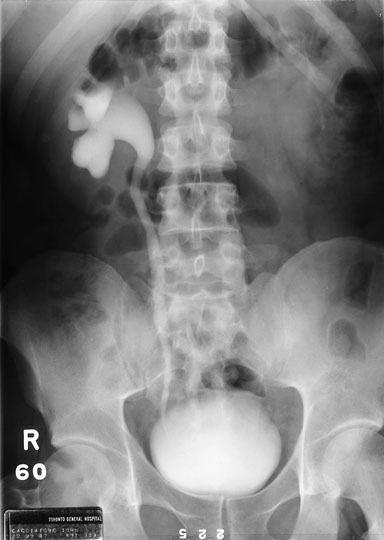
UPJ Obstruction
Congenital UPJ Obstruction & Hydronephrosis
Congenital utero-pelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction & hydronephrosis. This image demonstrates severe hydronephrosis of the right kidney. Retrograde pyelography demonstrates an obstruction at the UPJ. The obstruction in this patient was congenital.
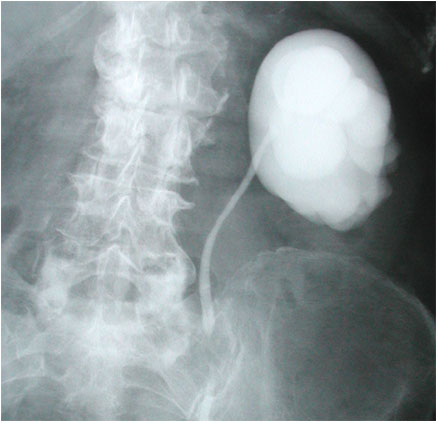
Stone CT
Non-contrast CT for renal colic.
Left Image: shows right-sided pelvicaliectasis relative to the left-sided renal collecting system.
Right Image: shows calculus in the distal right ureter as the cause.
[Courtesy of Dr. N. Jaffer]
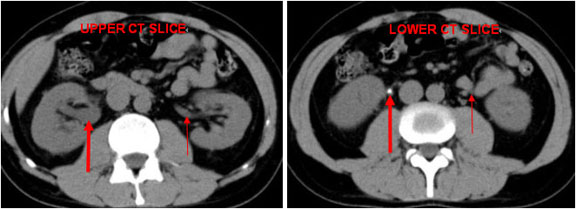
Hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis of left kidney on ultrasound caused by a left upper ureteric stone seen on abdominal X-ray (red arrow).
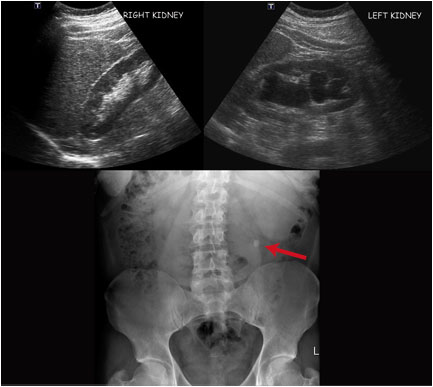
Uterus
Uterine Fibroid
Axial CT image of the female pelvis showing large uterine fibroid with the body of the uterus. (Courtesy of Dr. N. Jaffer)
Female Pelvis – US
Normal Female Pelvis (US)
Transabdominal ultrasound showing normal bladder, uterus and ovaries. (Courtesy of Dr. N. Jaffer)
Female Pelvis – MRI
Normal Female Pelvis (MRI)
Sagittal MRI of the female pelvis. (Courtesy of Dr. N. Jaffer)
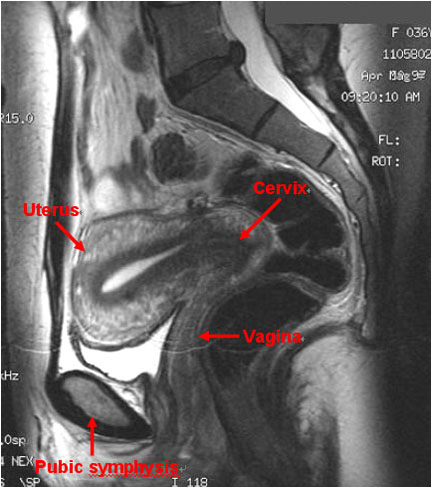
Bony Pelvis
Pelvic AP radiographs showing the male (left) and female (right) bony pelvis. Note that the male pelvis is narrower, with a “heart-shaped” pelvic inlet, while the female is wider, with a circular or oval-shaped pelvic inlet. (Courtesy of Dr. N. Jaffer)
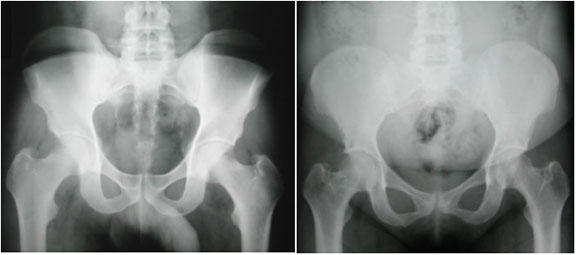
Ovaries
Ultrasound Image of Polycystic Ovaries
Note the cystic appearance resembling a “string of black pearls.”
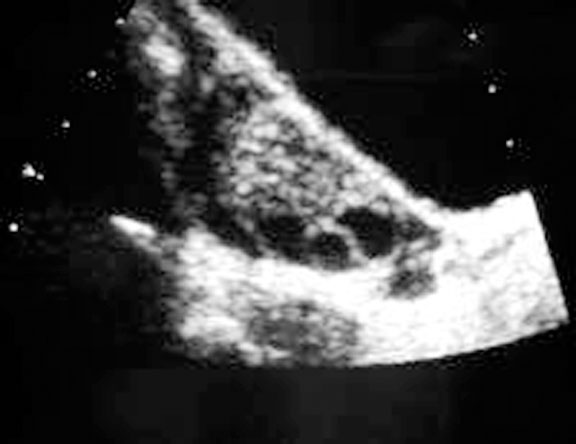
Triquetral Fracture
It is either a dorsal avulsion or body fracture. Look for tenderness dorsally, distal to ulnar styloid.
Scaphoid Fracture
Scaphoid fracture of the wrist. The most common carpal fracture. Look for tenderness at the anatomic snuff box. Wrist x-ray is often negative.
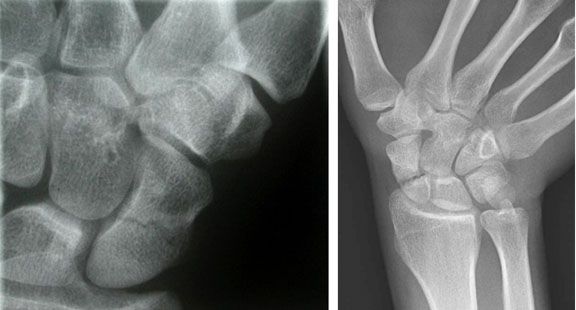
Thalamic Glioma
Axial CT with contrast showing a ring enhancing lesion over the left thalamic region with central necrosis. [Courtesy of Dr. J. Spears]
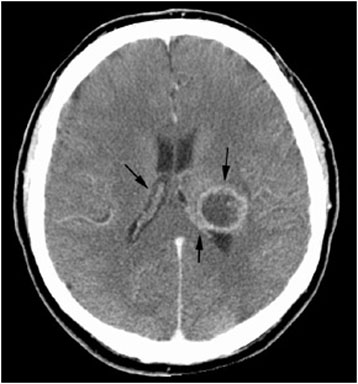
Posterior Fossa Meningioma
T1-weighted coronal MRI with contrast. A large tumour is highlighted in the right posterior fossa and bilateral dilatation of the lateral ventricles is evident (likely secondary to compression of the 4th ventricle or Sylvian aqueduct). [Courtesy of Dr. J. Spears]
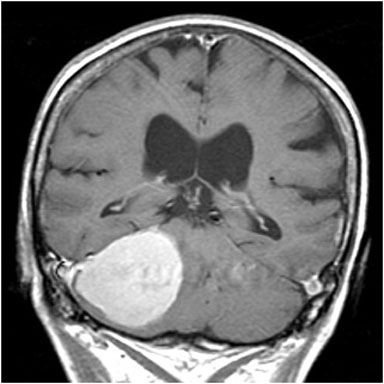
Pituitary Adenoma
Multiple views of post-contrast CT image of a pituitary adenoma. The saggital view demonstrates the transphenoidal approach for surgery. [Courtesy of Dr. J. Spears]
Monochorionic Twins
Monochorionic, diamniotic twins T sign
(Courtesy of Dr. Seaward and Dr. Ryan, Mt Sinai Hospital)
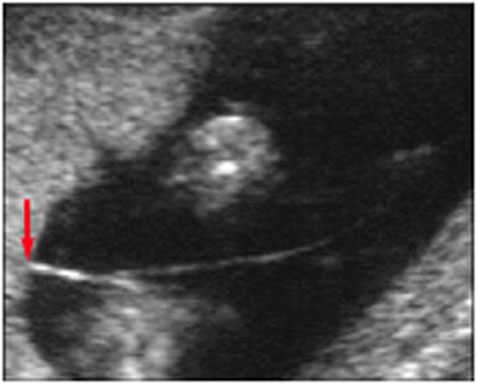
Dichorionic Twins
Dichorionic, diamniotic twins lamdba sign
(Courtesy of Dr. Seaward and Dr. Ryan, Mt Sinai Hospital)
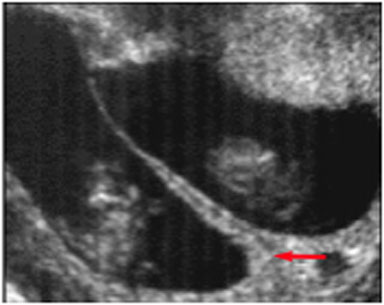
Placenta Previa
Placenta (P) covers the os. Crosses (+) approximate the cervical length and the bladder (B) is seen on the right.
(Courtesy of Dr. Seaward and Dr. Ryan, Mt Sinai Hospital)
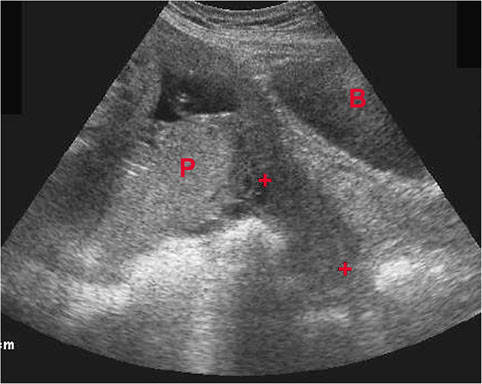
Maxillary Sinusitis
Axial CT scan of maxillary sinusitis. Note air-fluid level in left maxillary sinus. (Courtesy of Dr. A. Waltzman)
Choanal Atresia
Axial CT scan of choanal atresia (arrow indicated bony obstructive plate). (Courtesy of Dr. Papsin, HSC)
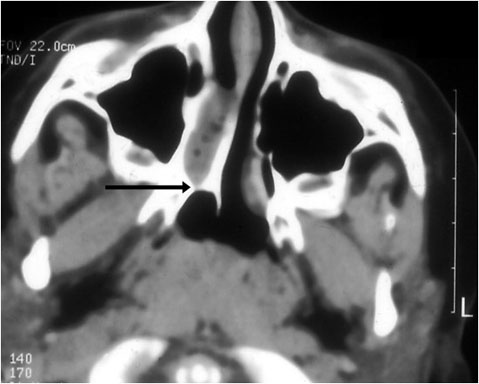
Carcinoma
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
Axial CT scan of expansive tumour arising in the nasopharynx and causing bilateral nasal obstruction. (Courtesy of Dr. Irish, UHN)
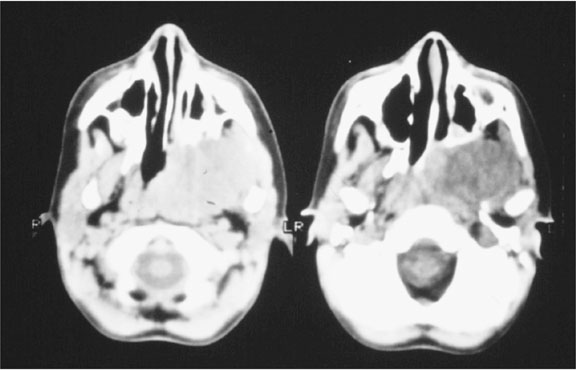
Adenotonsillar Hypertrophy
Lateral plain film. Note significant tonsillar (large arrow) and adenoid (small arrow) hypertrophy leading to significant narrowing of the nasal and oral airways. (Courtesy of Dr. Papsin, HSC)
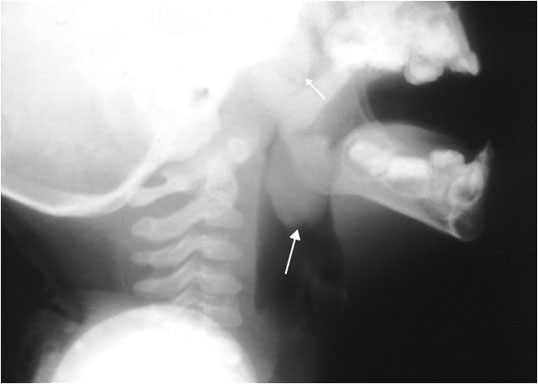
Tetralogy of Fallot
Note the characteristic chest x-ray finding of a boot-shaped heart. (Courtesy Dr. E. Ng)
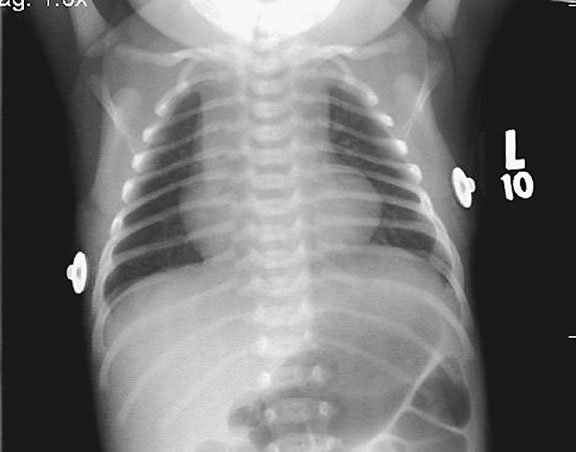
Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Note the dilated loops of bowel and pneumatosis intestinalis. (Courtesy Dr. E. Ng)