Browse by specialty
- Anesthesia and Perioperative
- Cardiology & Cardiovascular System
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Dermatology
- Diagnostic Imaging
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethical, Legal, and Organizational Medicine
- Family Medicine
- Gastroenterology
- General Surgery
- Geriatric Medicine
- Gynecology
- Haematology
- Infectious Disease
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Obstetrics
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pediatrics
- Plastic Surgery
- Population and Community Health
- Psychiatry
- Respirology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
Geriatric Medicine
Full-Colour Atlas
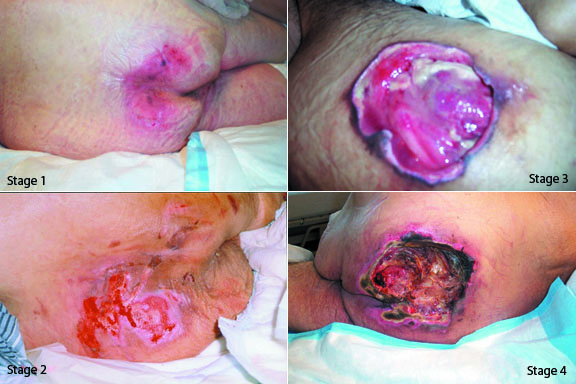
Stages 1-4 All views
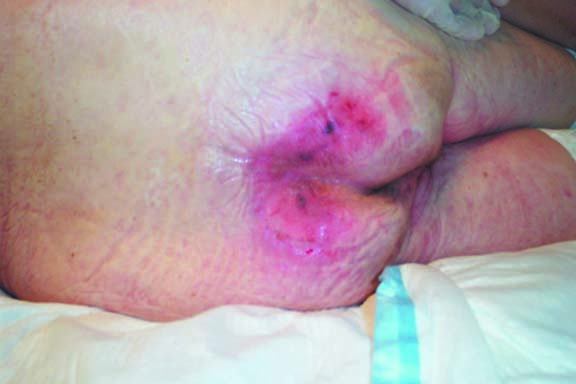
Stage 1 – Nonblanchable erythema of intact skin.
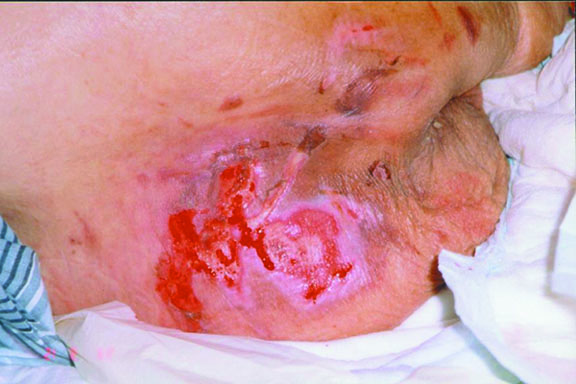
Stage 2 – Partial thickness superficial skin loss involving epidermis and/or dermis that usually presents as an abrasion, blister, or shallow crater.
Stage 3 – Full thickness skin loss with damage or necrosis of subcutaneous tissue that may extend down to, but not through, underlying fascia, presenting as a deep crater with or without undermining of adjacent tissue.
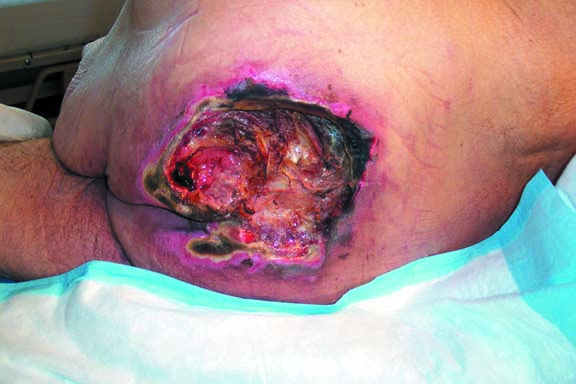
Stage 4 – Full thickness skin loss with extensive destruction, tissue necrosis, or damage to muscle, bone, or supporting structures (e.g. tendon or joint capsule), and may be present with undermining and sinus tracts.
Stage 4
Full thickness skin loss with extensive destruction, tissue necrosis, or damage to muscle, bone, or supporting structures (e.g. tendon or joint capsule), and may be present with undermining and sinus tracts. (Courtesy of Rola Maghabaghab, RN)
Stage 3
Full thickness skin loss with damage or necrosis of subcutaneous tissue that may extend down to, but not through, underlying fascia, presenting as a deep crater with or without undermining of adjacent tissue. (Courtesy of Rola Maghabaghab, RN)
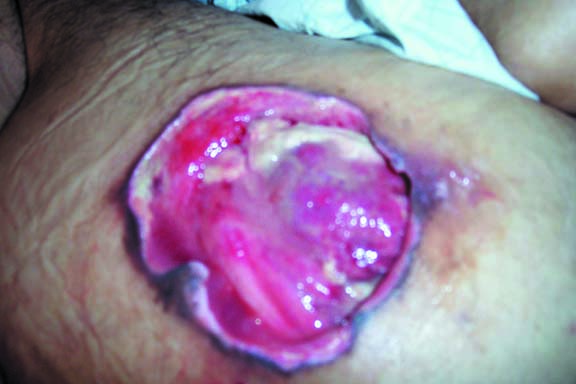
Stage 2
Partial thickness superficial skin loss involving epidermis and/or dermis that usually presents as an abrasion, blister, or shallow crater. (Courtesy of Rola Maghabaghab, RN)